A human high-fidelity DNA polymerase holoenzyme has a wide range of lesion bypass activities
- PMID: 40671520
- PMCID: PMC12266135
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf646
A human high-fidelity DNA polymerase holoenzyme has a wide range of lesion bypass activities
Abstract
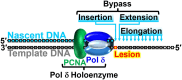
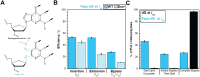
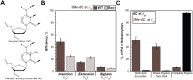
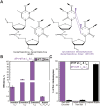
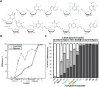
During replication, lagging strand lesions are initially encountered by high-fidelity DNA polymerase (pol) holoenzymes comprised of pol δ and the PCNA sliding clamp. To proceed unhindered, pol δ holoenzymes must bypass lesions without stalling. This entails dNMP incorporation opposite the lesion (insertion) and the 5' template deoxynucleotide (extension). Historically, it was viewed that high-fidelity pol holoenzymes stall upon encountering lesions, activating DNA damage tolerance pathways that are ultimately responsible for lesion bypass. Our recent study of four prominent lesions revealed that human pol δ holoenzymes support insertion and/or bypass for multiple lesions and the extent of these activities depends on the lesion and pol δ proofreading. In the present study, we expand these analyses to other prominent lesions. Collectively, analyses of 10 lesions from both studies reveal that the insertion and bypass efficiencies of pol δ holoenzymes each span a complete range (0%-100%). Consequently, the fates of pol δ holoenzymes upon encountering lesions are quite diverse. Furthermore, pol δ proofreading promoted holoenzyme progression at 7 of the 10 lesions and did not deter progression at any. Altogether, the results significantly alter our understanding of the replicative capacity of high-fidelity pol holoenzymes and their functional role(s) in lesion bypass.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


Update of
-
A human high-fidelity DNA polymerase holoenzyme has a wide range of lesion bypass activities.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 17:2024.10.14.618244. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.14.618244. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jul 8;53(13):gkaf646. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf646. PMID: 39464047 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
A human high-fidelity DNA polymerase holoenzyme has a wide range of lesion bypass activities.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 17:2024.10.14.618244. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.14.618244. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jul 8;53(13):gkaf646. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf646. PMID: 39464047 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Replication protein A dynamically re-organizes on primer/template junctions to permit DNA polymerase δ holoenzyme assembly and initiation of DNA synthesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jul 22;52(13):7650-7664. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae475. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38842913 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking of progressing human DNA polymerase δ holoenzymes reveals distributions of DNA lesion bypass activities.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Sep 23;50(17):9893-9908. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac745. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36107777 Free PMC article.
-
Bulk synthesis and beyond: The roles of eukaryotic replicative DNA polymerases.DNA Repair (Amst). 2024 Sep;141:103740. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2024.103740. Epub 2024 Jul 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2024. PMID: 39096696 Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

