Factors Influencing Cardiac Rehabilitation Compliance in Elderly Myocardial Infarction Patients and the Development of a Nomogram Prediction Model
- PMID: 40671941
- PMCID: PMC12264351
- DOI: 10.2147/PPA.S529753
Factors Influencing Cardiac Rehabilitation Compliance in Elderly Myocardial Infarction Patients and the Development of a Nomogram Prediction Model
Abstract
Objective: To explore the influencing factors of cardiac rehabilitation compliance in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and to construct a nomogram prediction model.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on 239 elderly AMI patients admitted to our hospital from April 2022 to April 2024. The patients were randomly assigned into a modeling group (167 cases) and a validation group (72 cases) in a 7:3 ratio. The modeling group was separated into a good compliance group and a poor compliance group based on their compliance with cardiac rehabilitation.
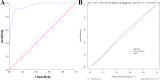
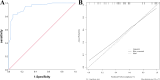
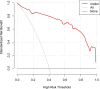
Results: Among the 167 patients in the modeling group, 67 had poor compliance, with an incidence rate of 40.12%. Multivariate logistic regression revealed that age, educational level, perception of disease, anxiety and depression, social support, and medical staff supervision were risk factors for cardiac rehabilitation compliance in elderly AMI patients (P<0.05). The AUC values of the modeling and validation groups were 0.955 and 0.937, respectively. The slope of the calibration curve was close to 1, and the H-L test showed χ 2=7.863 and 7.453, with P=0.789 and 0.775, indicating good consistency. DCA curve showed that when the high-risk threshold probability was between 0.08 and 0.93, the nomogram model had a high clinical value.
Conclusion: Age, educational level, perception of the disease, anxiety and depression, social support, and medical staff supervision are the influencing factors of cardiac rehabilitation compliance in elderly AMI patients. The nomogram model constructed based on this has good discrimination and consistency, and can predict cardiac rehabilitation compliance.
Keywords: cardiac rehabilitation; compliance; influencing factors; myocardial infarction; nomogram.
© 2025 Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Analysis of risk factors for reflux esophagitis after proximal gastrectomy in patients with proximal gastric cancer and construction of a nomogram prediction model.J Gastrointest Surg. 2025 Aug;29(8):102114. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2025.102114. Epub 2025 Jun 9. J Gastrointest Surg. 2025. PMID: 40499890
-
Are Current Survival Prediction Tools Useful When Treating Subsequent Skeletal-related Events From Bone Metastases?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Sep 1;482(9):1710-1721. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003030. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38517402
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
The comparative and added prognostic value of biomarkers to the Revised Cardiac Risk Index for preoperative prediction of major adverse cardiac events and all-cause mortality in patients who undergo noncardiac surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 21;12(12):CD013139. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013139.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34931303 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

