Identifying Predictive Factors for Complete Skin Clearance at Week 52 by Deucravacitinib in Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis: A Prospective Observational Study
- PMID: 40672022
- PMCID: PMC12264360
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.86044
Identifying Predictive Factors for Complete Skin Clearance at Week 52 by Deucravacitinib in Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis: A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Deucravacitinib, an oral selective tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitor, is effective for moderate-to-severe psoriasis. However, not all patients can achieve complete skin clearance (CSC) by deucravacitinib even after long-term treatment (one year). Therefore, we sought to determine predictive baseline factors of achieving CSC (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score 0) at week 52.
Methods: In this prospective single‑center study (December 2022 - February 2025), we enrolled 77 patients aged ≥ 15 years and treated them with deucravacitinib 6 mg once daily. Baseline demographic, clinical, and laboratory factors were compared between patients who achieved CSC at week 52 and those who did not.
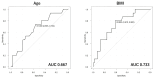
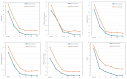
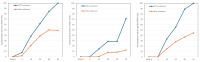
Results: Seventy-seven patients aged ≥ 15 years with moderate to severe psoriasis received deucravacitinib 6 mg once daily, and 15 patients achieved CSC at week 52. We compared patients' background factors and baseline clinical and laboratory indices between week 52 CSC achievers and non-achievers. The age (years) of week 52 CSC achievers (median: 55.0; IQR: 45.0-65.5) was significantly younger compared to non-achievers (median: 67.0; IQR: 55.3-76.0) (p = 0.0461, by Mann-Whitney U test; area under the curve (AUC) = 0.667). Additionally, the body mass index (BMI) of week 52 CSC achievers (median: 20.9; IQR: 18.3-22.9) was significantly lower compared to non-achievers (median: 23.6; IQR: 22.0-27.1) (p = 0.00571, by Mann-Whitney U test; AUC = 0.733). Compared to non-achievers, week 52 CSC achievers showed higher and faster improvements of nail, scalp, and genital lesions and quality of life, evaluated by the Dermatology Life Quality Index.
Conclusions: A BMI < 22.9 kg/m² and age < 61 years independently identify patients most likely to obtain CSC at week 52 with deucravacitinib. These cut‑offs can support early treatment selection and stratification in future prospective trials, facilitating personalized care for psoriasis.
Keywords: complete skin clearance; deucravacitinib; predictive factor; psoriasis; tyrosine kinase 2.
Copyright © 2025, Takahashi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Nippon Medical School Chiba Hokusoh Hospital issued approval H-2023-095. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (2004) and approved by the Ethics Committee of Nippon Medical School Chiba Hokusoh Hospital (protocol code H-2023-095) on December 7, 2023. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: Teppei Hagino, Hidehisa Saeki, and Naoko Kanda received lecture fees from Bristol Myers Squibb. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to be disclosed. Hidehisa Saeki is an Editorial Board member of the Journal of Dermatology and a co-author of this article. To minimize bias, he should be excluded from all editorial decision-making related to the acceptance of this article for publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Deucravacitinib, an oral selective allosteric tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitor, in patients from China mainland, Taiwan and South Korea with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a phase III randomized clinical trial.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Feb 18;192(3):402-409. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae406. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39437312 Clinical Trial.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Anti-TNF agents for paediatric psoriasis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 24;2015(11):CD010017. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010017.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26598969 Free PMC article.
-
Etanercept and efalizumab for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Nov;10(46):1-233, i-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta10460. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 17083854
References
-
- The TNF/IL-23/IL-17 axis—head-to-head trials comparing different biologics in psoriasis treatment. Ten Bergen LL, Petrovic A, Krogh Aarebrot A, Appel S. Scand J Immunol. 2020;92:0. - PubMed
-
- Chemokine receptors in the pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Mabuchi T, Chang TW, Quinter S, Hwang ST. J Dermatol Sci. 2012;65:4–11. - PubMed
-
- Epidermal CCR6+ γδ T cells are major producers of IL-22 and IL-17 in a murine model of psoriasiform dermatitis. Mabuchi T, Takekoshi T, Hwang ST. J Immunol. 2011;187:5026–5031. - PubMed
-
- Effectiveness of long-term bimekizumab treatment and predictive factors for responders in moderate-to-severe psoriasis: a 52-week real-world study. Hagino T, Saeki H, Fujimoto E, Kanda N. J Dermatol. 2025;52:317–328. - PubMed
-
- Global burden of psoriasis - comparison of regional and global epidemiology, 1990 to 2017. AlQassimi S, AlBrashdi S, Galadari H, Hashim MJ. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:566–571. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
