Long-term outcomes of indeterminate focal hepatic observations less than 20 mm followed up with gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (Gd-EOB-DTPA-MRI)
- PMID: 40672063
- PMCID: PMC12260963
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-2025-302
Long-term outcomes of indeterminate focal hepatic observations less than 20 mm followed up with gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (Gd-EOB-DTPA-MRI)
Abstract
Background: Indeterminate hepatic observations classified as Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) category 3 (LR-3) exhibit uncertain malignant potential and pose a diagnostic challenge during hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) surveillance. Although most LR-3 observations remain stable, recent studies have reported variable progression rates to HCC. The purpose of the present study was to investigate and assess the clinical outcomes and progression-associated factors of LR-3 observations less than 20 mm in high-risk patients, on follow-up with serial gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (Gd-EOB-MRI).
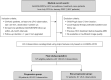
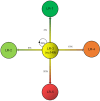
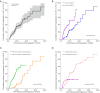
Methods: A retrospective review was conducted on 125 patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related cirrhosis who underwent Gd-EOB-MRI examinations at index and during follow-up. A total of 149 untreated LR-3 observations less than 20 mm in size were included in the study. Stepwise multivariate Cox proportional hazards model analysis was performed to identify the predictive risk factors for progression (upgraded to LR-4 or LR-5), including patient demographics and LI-RADS imaging features. Overall cumulative risk for progression was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method, and significant predictive risk factors were compared using the log-rank test.
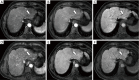
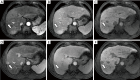
Results: Over a median follow-up period of 18.3 months (range, 2.7-78.5 months), the overall cumulative risk of progression for LR-3 observations was 41.6% (62/149) and was 1.3%, 9.5%, 17.3%, and 37.3% at 3, 6, 12, and 24 months, respectively. The multivariate analysis revealed three significant independent predictors of progression: non-rim arterial phase hyperenhancement (APHE) [hazard ratio (HR) =2.19; P=0.005], subthreshold growth (HR =2.78; P=0.001), and mild-to-moderate T2 hyperintensity (HR =5.25; P<0.001). LR-3 observations with non-rim APHE or mild-to-moderate T2 hyperintensity showed a significantly higher cumulative risk of progression (53.3% vs. 33.7% and 50.0% vs. 28.8%, respectively; both P<0.001), as well as a shorter median interval to LR category upgrade (14.7 vs. 18.9 months and 15.1 vs. 26.5 months, respectively; both P<0.001), compared to those without these features.
Conclusions: Non-rim APHE, subthreshold growth, and mild-to-moderate T2 hyperintensity were significantly associated with an increased risk of progression among high-risk patients with LR-3 observations.. In particular, the presence of non-rim APHE or mild-to-moderate T2 hyperintensity was linked to both a higher cumulative incidence of progression and a shorter median interval to LR category upgrade.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS); Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System category 3 (LR-3); follow-up; gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (Gd-EOB-DTPA-MRI).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-2025-302/coif). F.X. reports funding support from the Nantong University Special Research Fund for Clinical Medicine (No. EK2021017), outside the submitted work. S.M. reports funding support from Funding of University “Qinglan Project” in Jiangsu Province and Teaching Reform Research Project of Nantong University in 2024 (No. 2024E05), outside the submitted work. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term evolution of LR-2, LR-3 and LR-4 observations in HBV-related cirrhosis based on LI-RADS v2018 using gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023 Dec;48(12):3703-3713. doi: 10.1007/s00261-023-04016-7. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023. PMID: 37740759
-
Based on Gadolinium Ethoxybenzyl DTPA-Enhanced MRI: Diagnostic Performance of the Category-Modified LR-5 Criteria in Patients At Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241256859. doi: 10.1177/15330338241256859. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38780516 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of combining serum alpha-fetoprotein with LI-RADS v2018 on gadoxetate-enhanced MRI in the diagnosis and prognostication of hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur Radiol. 2025 Aug;35(8):4957-4966. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11418-2. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39930127
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound using SonoVue® (sulphur hexafluoride microbubbles) compared with contrast-enhanced computed tomography and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the characterisation of focal liver lesions and detection of liver metastases: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2013 Apr;17(16):1-243. doi: 10.3310/hta17160. Health Technol Assess. 2013. PMID: 23611316 Free PMC article.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
