Evaluating the combined diagnostic power of alpha-fetoprotein and protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 40672067
- PMCID: PMC12261048
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-2024-863
Evaluating the combined diagnostic power of alpha-fetoprotein and protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths globally, largely due to delayed diagnosis. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), a traditional biomarker for HCC, suffers from limited sensitivity and specificity, particularly in early-stage disease. Protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II (PIVKA-II) has emerged as a promising complementary marker. This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of AFP and PIVKA-II, individually and in combination, in HCC detection.
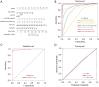
Methods: A total of 210 HCC patients and 270 chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients were enrolled between June 2021 and February 2023. Additionally, 91 HCC patients and 88 CHB patients were included as a validation cohort. Serum levels of AFP and PIVKA-II were measured, and their diagnostic efficacy was assessed using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. A multivariate logistic regression model incorporating clinical features and biomarkers was developed and validated. A meta-analysis of relevant studies was also conducted to further confirm the diagnostic value of AFP.
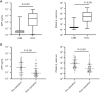
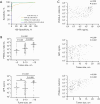
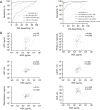
Results: PIVKA-II levels were significantly higher in HCC patients compared to CHB controls and showed superior diagnostic performance [area under the curve (AUC) =0.970] compared to AFP (AUC =0.890). The combination of AFP and PIVKA-II significantly improved sensitivity (98.6%) and specificity (91.1%). A predictive model integrating AFP, PIVKA-II, age, sex, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and albumin (ALB) demonstrated excellent diagnostic accuracy (AUC =0.995) and was successfully validated (AUC =0.986). Meta-analysis supported AFP as a reliable biomarker for HCC, although with heterogeneity across studies. PIVKA-II was also effective in monitoring treatment response, with postoperative levels markedly decreasing in patients undergoing hepatectomy.
Conclusions: PIVKA-II offers superior diagnostic accuracy for HCC and complements AFP to enhance early detection, especially in AFP-insensitive cases. The combined biomarker strategy and predictive model provide a robust framework for clinical screening and early intervention. Integration of PIVKA-II into routine diagnostic workflows could improve patient outcomes and reduce diagnostic delays in HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); alpha-fetoprotein (AFP); diagnostic biomarkers; early detection; protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II (PIVKA-II).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-2024-863/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
