This is a preprint.
Nuclear and cytosolic J-domain proteins provide synergistic control of Hsf1 at distinct phases of the heat shock response
- PMID: 40672285
- PMCID: PMC12265559
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.04.14.648540
Nuclear and cytosolic J-domain proteins provide synergistic control of Hsf1 at distinct phases of the heat shock response
Abstract
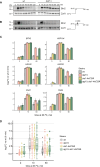
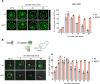
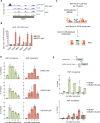
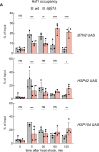
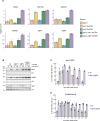
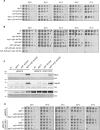
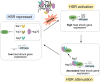
The heat shock response (HSR) is the major defense mechanism against proteotoxic stress in the cytosol and nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Initiation and attenuation of the response are mediated by stress-dependent regulation of heat shock transcription factors (HSFs). Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a single HSF (Hsf1), facilitating the analysis of HSR regulation. Hsf1 is repressed by Hsp70 chaperones under non-stress conditions, and becomes activated under proteotoxic stress, directly linking protein damage and its repair to the HSR. J-domain proteins (JDPs) are essential for targeting of Hsp70s to their substrates, yet the specific JDP(s) regulating Hsf1 and connecting protein damage to HSR activation remain unclear. Here we show that the yeast nuclear JDP Apj1 primarily controls the attenuation phase of the HSR by promoting Hsf1's displacement from heat shock elements in target DNA. In apj1Δ cells, HSR attenuation is significantly impaired. Additionally, yeast cells lacking both Apj1 and the major JDP Ydj1 exhibit increased HSR activation even in non-stress conditions, indicating their distinct regulatory roles. Apj1's role in both nuclear protein quality control and Hsf1 regulation underscores its role in directly linking nuclear proteostasis to HSR regulation. Together these findings establish the nucleus as key stress-sensing signaling hub.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SUMOylation is not a prerequisite for HSF1's role in stress protection and transactivation.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 5;15(1):24077. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08735-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40617887 Free PMC article.
-
The Heat Shock Response as a Condensate Cascade.J Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 15;436(14):168642. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168642. Epub 2024 Jun 5. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38848866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional memory dampens heat shock responses in yeast: functional role of Mip6 and its interaction with Rpd3.G3 (Bethesda). 2025 Aug 6;15(8):jkaf144. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaf144. G3 (Bethesda). 2025. PMID: 40537058 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear basket proteins Nup2 and Mlp1 drive heat shock-induced 3D genome restructuring downstream of transcriptional activation.J Biol Chem. 2025 Aug 6:110568. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110568. Online ahead of print. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40780415
-
A guide to heat shock factors as multifunctional transcriptional regulators.FEBS J. 2025 Aug;292(16):4133-4155. doi: 10.1111/febs.70139. Epub 2025 Jun 2. FEBS J. 2025. PMID: 40457168 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aparicio O, Geisberg JV, Sekinger E, Yang A, Moqtaderi Z, Struhl K (2005) Chromatin immunoprecipitation for determining the association of proteins with specific genomic sequences in vivo. Curr Protoc Mol Biol Chapter 21: Unit 21 23 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
