Hesperidin alleviates hypothyroidism-related cardiac dysfunction by targeting cardiac miRNAs, Nrf2/NF-κB signaling, oxidative stress and inflammation
- PMID: 40672362
- PMCID: PMC12263625
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1553992
Hesperidin alleviates hypothyroidism-related cardiac dysfunction by targeting cardiac miRNAs, Nrf2/NF-κB signaling, oxidative stress and inflammation
Abstract
Background: Hypothyroidism is a frequent endocrine health issue that is linked to adverse cardiovascular events. Accumulating evidence suggests that thyroid hormone replacement does not fully reverse the cardiovascular complications associated with the disease despite normalization of serum thyroid hormone levels, indicating a need for adjunctive, complementary, or alternative therapies. Hesperidin (HSD) has diverse pharmacological activities, however, its therapeutic potential on the crosstalk between hypothyroidism and cardiac dysfunction has not been previously reported.
Methods: This study aimed to investigate the cardioprotective efficacy of HSD on carbimazole (CMZ)-induced hypothyroidism in rats in comparison to the traditional thyroid hormone replacement therapy; levothyroxine (LT4). Male Wistar albino rats were divided into four groups: normal control (NC), CMZ (30 mg/kg), CMZ + HSD (30 mg/kg CMZ + 200 mg/kg HSD), and CMZ + LT4 (30 mg/kg CMZ + 0.045 mg/kg). All doses were given orally and daily for 9 weeks.
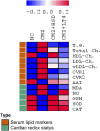
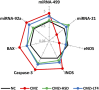
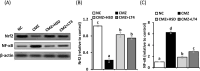
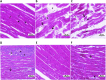
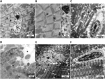
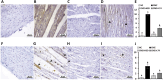
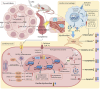
Results: CMZ intake resulted in a significant decrease in thyroid hormones (THs) levels with a subsequent increase in serum thyroid stimulating hormone and cardiac enzymes activities, dyslipidemia, and body weight gain. Cardiac tissues revealed marked oxidative stress, inflammation, and structural degenerative lesions. As well, cardiac expression of miRNAs-92a and -499 was elevated while that of miRNA-21 was depleted, reflecting an interdependence between hypothyroidism and the development of cardiac dysfunction. Despite HSD and LT4 effectively alleviating the THs profile, only HSD offered substantial protection from hypothyroidism-associated cardiac inflammation and injury through its potent impact on the transcriptional miRNAs level and Nrf2/NF-κB protein expression (key regulators of the redox biomarkers and the inflammatory mediators).
Conclusion: HSD provides dual thyroprotective and cardioprotective effects that enhance THs bioavailability and functionality in the cardiovascular system.
Keywords: cardiac dysfunction; hesperidin; hypothyroidism; inflammation; miRNAs; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2025 Gaber, Abdel-Moneim, Abdel-Reheim, Allam, Abdul-Hamid and Hosni.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 5;2016(5):CD003725. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003725.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27149418 Free PMC article.
-
Genistein Enhances the Beneficial Effects of Exercise on Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Balance and Cardiomyopathy in Ovariectomized Diabetic Rats.Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2025;24(2):103-113. doi: 10.2174/0118715230305886240916105248. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39482917
-
Effectiveness of the fruit of Rosa odorata sweet var. gigantea (Coll. et Hemsl.) Rehd. et Wils in the protection and the healing of ethanol-induced rat gastric mucosa ulcer based on Nrf2/NF-κB pathway regulation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jan 10;282:114626. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114626. Epub 2021 Sep 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34517064
References
-
- Abdel-Moneim A., Mahmoud B., Mahmoud R. (2015). The beneficial effects of fish oil supplementation on hyperlipidemic and hypothyroid albino rats. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 8 (4), 328–333.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

