Rubinstein Taybi syndrome caused by EP300 gene mutation: what we learned from two cases and literature review
- PMID: 40672389
- PMCID: PMC12263406
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1588657
Rubinstein Taybi syndrome caused by EP300 gene mutation: what we learned from two cases and literature review
Abstract
Introduction: Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome is an extremely rare autosomal dominant genetic disease. The incidence of RSTS ranges from 1/100 000 to 125 000.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the phenotype and genotype of two children who were diagnosed with RSTS in Hunan Province Children's Hospital from January 2022 to December 2023. Clinical data of the children were collected. Whole-exome sequencing was performed on the children. The candidate variants were verified by Sanger sequencing in the pedigree, followed by pathogenicity analysis.
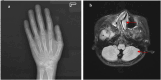
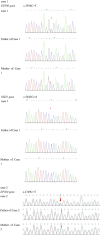
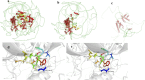
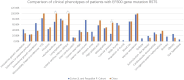
Results: The main clinical presentations of the two cases were growth retardation, special facial features, and mild intellectual disability. Three mutations were detected by exome sequencing, all of which were sporadic mutations verified by Sanger sequencing. In case 1, pathological mutations were detected in EP300 gene and NSD1 gene. A heterozygous mutation c. 3934C>T (p. Arg1312Ter) was detected in exon 24 of EP300 gene. A heterozygous mutation c. 5843G>A (p. Arg1948 His) was detected in exon 18 of NSD1 gene. In case 2, a heterozygous mutation (c.2749C>T) (p. Gln917 *) was detected in exon 14 of EP300 gene, which has not been reported in the literature so far. According to ACMG guidelines, this mutation was preliminarily determined to be pathogenic. Comparative analysis of phenotypic differences between the Chinese cohort and the Cohen JL and Fergelot P. cohorts revealed that arched eyebrows, downslanting palpebral fissures, and low-set ears were significantly more common in the Chinese population.
Discussion: EP300 gene c.2749C>T heterozygous mutation may be the genetic cause of Rubinstein Taybi syndrome. EP300 gene combined with NSD1 gene mutation may lead to atypical clinical presentations. These findings further enrich the variation spectrum of EP300 gene.
Keywords: EP300 gene; NSD1 gene; Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome; children; growth retardation.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wu, Zhao and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cohen J. L., Schrier Vergano S. A., Mazzola S., Strong A., Keena B., McDougall C., et al. (2020). EP300-related Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: highlighted rare phenotypic findings and a genotype-phenotype meta-analysis of 74 patients. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 182 (12), 2926–2938. 10.1002/ajmg.a.61883 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

