Relationship between nocturia, depression, and cognitive function and the mediating effects of nutritional indexes in older adults: data from NHANES 2011-2014
- PMID: 40672414
- PMCID: PMC12263384
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1533683
Relationship between nocturia, depression, and cognitive function and the mediating effects of nutritional indexes in older adults: data from NHANES 2011-2014
Abstract
Purpose: This study evaluated the correlation between nocturia, depression, and cognitive function in older adults and the mediating effect of albumin and hemoglobin on this correlation.
Methods: Data on nocturia, depression, and cognitive function from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2014 were analyzed by multiple logistic regression.
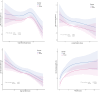
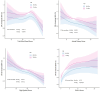
Results: The digit symbol score (DSS) and 9-Item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) scores were linearly and non-linearly correlated with nocturia risk (p < 0.05). Male/female-stratified analysis showed that animal fluency scores (AFS), DSS, and PHQ-9 scores were significantly correlated with the risk of nocturia in females (p < 0.05), and PHQ-9 scores were significantly associated with the risk of nocturia in males (p < 0.05). Albumin partially mediated the association of AFS, DSS, and PHQ-9 scores with nocturia risk in women and the relationship of PHQ-9 scores with nocturia risk in men. Hemoglobin partially mediated the relationship of AFS and DSS with nocturia risk in women and the association of PHQ-9 scores with nocturia risk in men.
Conclusion: Nocturia is positively associated with depression and cognitive impairment in older adults, especially in women. Nutrition partially mediates the relationship between nocturia, depression, and cognitive function. Thus, improving nutrition may decrease the risk of nocturia in older adults.
Keywords: albumin; cognitive function; depression; hemoglobin; nocturia; older adults.
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Wang, Wang, Wei and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cardiovascular disease and depression as mediators between red blood cell distribution width to albumin ratio and cognitive impairment in older adults.Front Physiol. 2025 Jun 11;16:1587635. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1587635. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40568468 Free PMC article.
-
The association between hearing loss and depression in the China health and retirement longitudinal study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20537. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05749-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595946 Free PMC article.
-
NHANES 2005-2018 data reveal high albumin-bilirubin scores are associated with depression.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):660. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-07082-x. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40597971 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological therapies for treatment-resistant depression in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 14;5(5):CD010558. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010558.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29761488 Free PMC article.
-
Anticholinergic deprescribing interventions for reducing risk of cognitive decline or dementia in older adults with and without prior cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Dec 8;12(12):CD015405. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015405.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38063254 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

