This is a preprint.
GlaucoRAG: A Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Model for Expert-Level Glaucoma Assessment
- PMID: 40672509
- PMCID: PMC12265780
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.07.03.25330805
GlaucoRAG: A Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Model for Expert-Level Glaucoma Assessment
Abstract
Purpose: Purpose: Accurate glaucoma assessment is challenging because of the complexity and chronic nature of the disease; therefore, there is a critical need for models that provide evidence-based, accurate assessment. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the capabilities of a glaucoma specialized Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework (GlaucoRAG) that leverages a large language model (LLM) for diagnosing glaucoma and answering to glaucoma specific questions.
Design: Evaluation of diagnostic capabilities and knowledge of emerging technologies in glaucoma assessment.
Participants: Detailed case reports from 11 patients and 250 multiple choice questions from the Basic and Clinical Science Course (BCSC) Self-Assessment were used to test the LLM based GlaucoRAG. No human participants were involved.
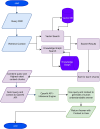
Methods: We developed GlaucoRAG, a RAG framework leveraging GPT-4.5-PREVIEW integrated with the R2R platform for automated question answering in glaucoma. We created a glaucoma knowledge base comprising more than 1,800 peer-reviewed glaucoma articles, 15 guidelines and three glaucoma textbooks. The diagnostic performance was tested on case reports and multiple-choice questions. Model outputs were compared with the independent answers of three glaucoma specialists, DeepSeek-R1, and GPT-4.5-PREVIEW (without RAG). Quantitative performance was further assessed with the RAG Assessment (RAGAS) framework, reporting faithfulness, context precision, context recall, and answer relevancy.
Main outcome measures: The primary outcome measure was GlaucoRAG's diagnostic accuracy on patient case reports and percentage of correct responses to the BCSC Self-Assessment glaucoma items, compared with the performance of glaucoma specialists and two benchmark LLMs. Secondary outcomes included RAGAS sub scores.
Results: GlaucoRAG achieved an accuracy of 81.8% on glaucoma case reports, compared with 72.7% for GPT-4.5-PREVIEW and 63.7% for DeepSeek-R1. On glaucoma BCSC Self-Assessment questions, GlaucoRAG achieved 91.2% accuracy (228 / 250), whereas GPT-4.5-PREVIEW and DeepSeek-R1 attained 84.4% (211 / 250) and 76.0% (190 / 250), respectively. The RAGAS evaluation returned an answer relevancy of 91%, with 80% context recall, 70% faithfulness, and 59% context precision.
Conclusions: The glaucoma-specialized LLM, GlaucoRAG, showed encouraging performance in glaucoma assessment and may complement glaucoma research and clinical practice as well as question answering with glaucoma patients.
Keywords: Glaucoma; Glaucoma Specialized RAG (GlaucoRAG); Large Language Mdoel (LLM); Question Answering (QA); Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leveraging Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models for Dietary Recommendations With Traditional Chinese Medicine's Medicine Food Homology: Algorithm Development and Validation.JMIR Med Inform. 2025 Aug 21;13:e75279. doi: 10.2196/75279. JMIR Med Inform. 2025. PMID: 40840437 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing health coaching: A comparative study of large language model and health coaches.Artif Intell Med. 2024 Nov;157:103004. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2024.103004. Epub 2024 Oct 19. Artif Intell Med. 2024. PMID: 39454500
-
Improving automated deep phenotyping through large language models using retrieval-augmented generation.Genome Med. 2025 Aug 18;17(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s13073-025-01521-w. Genome Med. 2025. PMID: 40826123 Free PMC article.
-
Fornix-based versus limbal-based conjunctival trabeculectomy flaps for glaucoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 25;11(11):CD009380. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009380.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Aug 26;8:CD009380. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009380.pub3. PMID: 26599668 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Madadi Yeganeh, Delsoz Mohammad, Khouri Albert S., Boland Michael, Grzybowski Andrzej, and Yousefi Siamak. Applications of artificial intelligence-enabled robots and chatbots in ophthalmology: recent advances and future trends. Current Opinion in Ophthalmology, 35(3), 2024. - PMC - PubMed
-
N2 - Purpose of review Recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and chatbots have brought these technologies to the forefront of medicine, particularly ophthalmology. These technologies have been applied in diagnosis, prognosis, surgical operations, and patient-specific care in ophthalmology. It is thus both timely and pertinent to assess the existing landscape, recent advances, and trajectory of trends of AI, AI-enabled robots, and chatbots in ophthalmology. Recent findings Some recent developments have integrated AI enabled robotics with diagnosis, and surgical procedures in ophthalmology. More recently, large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT have shown promise in augmenting research capabilities and diagnosing ophthalmic diseases. These developments may portend a new era of doctor-patient-machine collaboration. Summary Ophthalmology is undergoing a revolutionary change in research, clinical practice, and surgical interventions. Ophthalmic AI-enabled robotics and chatbot technologies based on LLMs are converging to create a new era of digital ophthalmology. Collectively, these developments portend a future in which conventional ophthalmic knowledge will be seamlessly integrated with AI to improve the patient experience and enhance therapeutic outcomes.
-
- Yousefi Siamak, Elze Tobias, Pasquale Louis R., Saeedi Osamah, Wang Mengyu, Shen Lucy Q., Wellik Sarah R., De Moraes Carlos G., Myers Jonathan S., and Boland Michael V.. Monitoring Glaucomatous Functional Loss Using an Artificial Intelligence–Enabled Dashboard. Ophthalmology, 127(9):1170–1178, September 2020. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources