Modified Huanjingjian Prevents Chemotherapy-Induced Alopecia by Inhibiting Genomic DNA Methylation of the Wnt Signaling Pathway in Mice
- PMID: 40672523
- PMCID: PMC12264502
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S523809
Modified Huanjingjian Prevents Chemotherapy-Induced Alopecia by Inhibiting Genomic DNA Methylation of the Wnt Signaling Pathway in Mice
Abstract
Aim: Cyclophosphamide (CTX), a cornerstone in breast cancer combination chemotherapy, frequently induces adverse effects including myelosuppression, gastrointestinal disturbances, hepatic impairment, and alopecia. Chemotherapy-induced alopecia severely impacts patients' quality of life and psychological well-being. Modified Huanjingjian (MHJJ), a traditional Chinese herbal formula, demonstrates clinical efficacy in alleviating chemotherapy-related side effects, yet its mechanisms against CTX-induced alopecia remain uncharacterized. And our main aim was to explore the efficacy and the mechanism of MHJJ in mice.
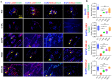
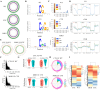
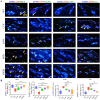
Methods: UPLC-QE-Orbitrap-MS characterized MHJJ's chemical composition. A CTX-induced alopecia murine model was established. Systemic toxicity was evaluated through body weight monitoring, automated biochemical analysis (ALT/AST levels), and hematological profiling (WBC/PLT counts). Hair follicle histopathology was assessed via H&E staining. IHC and IF staining quantified proliferation markers and hair follicle stem cell (HFSC) biomarkers. Reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) was used to map DNA methylation patterns. Wnt pathway dynamics were analyzed through qRT-PCR and IF staining.
Results: We identified 110 bioactive compounds in MHJJ. MHJJ intervention attenuated alopecia severity, restored follicular architecture, and increased follicular density compared to CTX monotherapy (p<0.05). HFSC proliferation markers (Ki67/CD34) showed significant upregulation, while apoptosis markers (Caspase-3) were suppressed. RRBS revealed MHJJ-mediated hypomethylation in differentially methylated regions, with gene body methylation constituting 60% of total methylation changes. Methylation-modulated genes predominantly localized to Wnt signaling pathways: MHJJ enhanced Wnt3/Wnt10a expression while suppressing Cer1/Axin1. Corresponding methylation reductions at promoter and gene body regions were confirmed at mRNA and protein levels.
Conclusion: MHJJ mitigates CTX-induced alopecia through epigenetic regulation of HFSCs, specifically via DNA hypomethylation-mediated activation of Wnt3/Wnt10a and suppression of Cer1/Axin1. This mechanism promotes follicular regeneration by restoring Wnt signaling homeostasis, positioning MHJJ as a promising adjuvant for chemotherapy-induced alopecia management.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Wnt signaling pathway; chemotherapy-induced alopecia; hair follicle; traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2025 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Shen-Ying-Yang-Zhen formula promotes angiogenesis around hair follicles, alleviates oxidative stress, and inhibits hair follicle apoptosis through the VEGF/Akt/Caspase-9 signaling axis.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:156963. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156963. Epub 2025 Jun 15. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40543232
-
Salvia miltiorrhiza extract ameliorated ovarian damage induced by cyclophosphamide in mice by multidimensional mechanisms.J Ovarian Res. 2025 Jul 11;18(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s13048-025-01727-x. J Ovarian Res. 2025. PMID: 40646602 Free PMC article.
-
Galactin-8 DNA methylation mediates macrophage autophagy through the MAPK/mTOR pathway to alleviate atherosclerosis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):603. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-85036-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747459 Free PMC article.
-
Taxane monotherapy regimens for the treatment of recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 12;7(7):CD008766. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008766.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866378 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicine for oesophageal cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jan 22;2016(1):CD004520. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004520.pub7. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26799001 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gumusay O, Renslo JR, Wabl CA, et al. A phase Ib/II study of eribulin with cyclophosphamide (EC) in patients (pts) with advanced breast cancer (ABC). J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(15–suppl):e13079–e13079. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15-suppl.e13079 - DOI
-
- Farishta M, Deepak V, Parmar M, Winters S. Severe cyclophosphamide-induced pneumonitis in a patient with breast cancer. Chest. 2019;156(4):A1506. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.08.1333 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

