Optimizing basil production and fertilizer use efficiency with consortia of plant growth-promoting bacteria
- PMID: 40672559
- PMCID: PMC12263919
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1591969
Optimizing basil production and fertilizer use efficiency with consortia of plant growth-promoting bacteria
Abstract
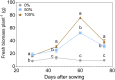
The basil, a widely cultivated aromatic plant, plays a crucial role in various industries but relies heavily on synthetic fertilizers, which contribute to environmental pollution. Plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) offer a sustainable alternative to reduce reliance on synthetic fertilizers. In this study, three PGPB consortia and one single-strain inoculant were evaluated under reduced nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization to assess their effects on biomass production, photosynthetic efficiency, and nutritional quality. The results showed that consortium comprising Herbaspirillum sp., Azospirillum brasilense, and Rhizobium leguminosarum, as well as the consortium with Rhizobium sp. and Azotobacter chroococcum, significantly increased fresh biomass production-by over than 130%-compared to non-inoculated plants. Similarly, inoculation with 50% fertilization increased nitrogen and potassium uptake by over 50% compared to receiving the complete recommended fertilization without inoculation, while phosphorus uptake increased by more than 28% relative to the same control. These findings indicate that PGPB consortia offer not only an environmentally sustainable alternative to conventional fertilizers but also an effective strategy for enhancing biomass production and improving nutrient uptake in basil crops.
Keywords: Ocimum basilicum L.; consortium; fertilization reduction; nutrient uptake. 2; photosynthesis.
Copyright © 2025 Beltrán-Medina, Toro-Tobón, Mendoza-Labrador, Quintero-Beyoda, Bermudez-Cordoba and Estrada-Bonilla.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors JB-M, GT-T, JM-L, GE-B were employed by Colombian Corporation for Agricultural Research AGROSAVIA. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handlingeditor CHM declared a past co-authorship with the author GE-B.
Figures





References
-
- Alhasan A. S., Al-Ameri D. T., Al-Baldawy M. S., Abbas M. K., Hasan H. H. (2020). ‘Influence of foliar application of NPK on growth, essential oil and seed yield of Basil (Ocimum basilicum cv. Dolly). Plant Arch. 20, 2959–2962.
-
- Baldani J. I., Reis V. M., Videira S. S., Boddey L. H., Baldani V. L. D. (2014). The art of isolating nitrogen-fixing bacteria from non-leguminous plants using N-free semi-solid media: a practical guide for microbiologists. Plant Soil. 384, 413–431. doi: 10.1007/s11104-014-2186-6 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

