Effect of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 levels on pathogenic bacteria types in patients with advanced lung cancer and pulmonary infection during chemotherapy
- PMID: 40672607
- PMCID: PMC12261208
- DOI: 10.62347/GRGQ7128
Effect of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 levels on pathogenic bacteria types in patients with advanced lung cancer and pulmonary infection during chemotherapy
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) in patients with advanced lung cancer complicated by pulmonary infection during chemotherapy and their effects on the type of pathogenic bacteria.
Method: We retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 196 patients from Wuhan Hankou Hospital (January 2021-June 2024). The incidence of pulmonary infection was assessed, and the levels of IL-6 and IL-8 were compared across different infection severities and pathogenic bacteria types. Spearman correlation analysis was used to determine associations, and logistic regression was performed to identify factors influencing different pathogenic bacteria infections.
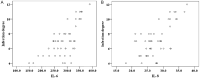
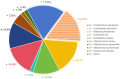
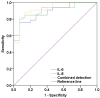
Result: The lung infection rate was 24.49% (48/196). Pathogenic bacteria included 36 strains (64.29%) of Gram-negative bacteria (G-) and 20 strains (35.71%) of Gram-positive bacteria (G+). The levels of IL-6 and IL-8 were significantly higher in infected patients than in uninfected patients (P < 0.05). These levels increased with the severity of infection and were positively correlated with the degree of infection. Elevated IL-6 and IL-8 levels were identified as independent risk factors for Gram-negative bacterial (G-) infections in patients with pulmonary infection. The combined AUC, sensitivity, and specificity of IL-6 and IL-8 were 0.925, 81.80%, and 93.33%, respectively.
Conclusion: In patients with advanced-stage lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy, elevated IL-6 and IL-8 levels were closely associated with pulmonary infection severity. Detection of these cytokines may help differentiate the types of pathogenic bacteria causing lung infections.
Keywords: Middle-late stage lung cancer; interleukin-6; interleukin-8; lung infection; pathogenic bacteria.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Lam DC, Liam CK, Andarini S, Park S, Tan DSW, Singh N, Jang SH, Vardhanabhuti V, Ramos AB, Nakayama T, Nhung NV, Ashizawa K, Chang YC, Tscheikuna J, Van CC, Chan WY, Lai YH, Yang PC. Lung cancer screening in asia: an expert consensus report. J Thorac Oncol. 2023;18:1303–1322. - PubMed
-
- Abu Rous F, Singhi EK, Sridhar A, Faisal MS, Desai A. Lung cancer treatment advances in 2022. Cancer Invest. 2023;41:12–24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
