Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) induced macrophage biphasic polarization regulated by dexamethasone in vivo
- PMID: 40672611
- PMCID: PMC12261169
- DOI: 10.62347/UGHK3747
Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) induced macrophage biphasic polarization regulated by dexamethasone in vivo
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate macrophage polarization dynamics in vivo after implantation of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) incorporated biomaterials, with a focus on dose-dependent effects and polarization modulation strategies.
Methods: A murine dorsal subcutaneous implantation model was utilized to analyze macrophage responses to varying concentrations of rhBMP-2-loaded biomaterials with or without dexamethasone (Dex). Polarization patterns were assessed through phenotypic characterization and cytokine expression profiling.
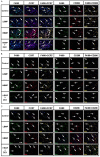
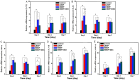
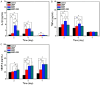
Results: Elevated rhBMP-2 concentrations amplified macrophage polarization activities, and concurrent activation of M1 and M2 polarization was observed accompanied by enhanced expression of both pro-inflammatory (M1-associated) and anti-inflammatory (M2-associated) cytokines. Dexamethasone co-administration effectively attenuated pro-inflammatory polarization patterns induced by high-dose rhBMP-2 implants while preserving regenerative cytokine expression.
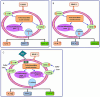
Conclusions: Optimized rhBMP-2 dosage facilitates a balanced macrophage polarization state, creating a pro-regenerative microenvironment through coordinated inflammatory resolution and tissue remodeling signals. For clinical applications requiring high rhBMP-2 doses, concurrent short-term anti-inflammatory therapy (e.g., dexamethasone) is recommended to mitigate excessive M1 polarization without compromising osteoinductive capacity.
Keywords: BMP-2; Macrophage; bio-material; dexamethasone; polarization.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


Similar articles
-
Leptin Enhances M1 Macrophage Polarization and Impairs Tendon-Bone Healing in Rotator Cuff Repair: A Rat Model.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 May 1;483(5):939-951. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003428. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 39982019
-
DS-Modified Paeoniflorin pH-Responsive Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Targeted Macrophage Polarization in a Rat Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 12;20:8967-8992. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S516434. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40671689 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanisms of Neiyiting Decoction in Preventing Postoperative Recurrence of Endometriosis by Inhibiting Macrophage M1 Polarization Through the TREM1/TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Mar 20;56(2):371-381. doi: 10.12182/20250360601. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40599271 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein use in spine surgery-complications and outcomes: a systematic review.Int Orthop. 2016 Jun;40(6):1309-19. doi: 10.1007/s00264-016-3149-8. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Int Orthop. 2016. PMID: 26961193
-
Effectiveness and harms of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in spine fusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Intern Med. 2013 Jun 18;158(12):890-902. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-158-12-201306180-00006. Ann Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23778906
References
-
- Rundle CH, Wang H, Yu H, Chadwick RB, Davis EI, Wergedal JE, Lao KH, Mohan S, Ryaby JT, Bylink DJ. Microarray analysis of gene expression during the inflammation and endochondral bone formation stages of rat femur fracture repair. Bone. 2006;38:521–529. - PubMed
-
- Sun JL, Jiao K, Niu LN, Jiao Y, Song Q, Shen LJ, Tay FR, Chen JH. Intrafibrillar silicified collagen scaffold modulates monocyte to promote cell homing, angiogenesis and bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2017;113:203–216. - PubMed
-
- Cooper PR, Takahashi Y, Graham LW, Simon S, Imazato S, Smith AJ. Inflammation-regeneration interplay in the dentine-pulp complex. J Dent. 2010;38:687–697. - PubMed
-
- Goertz O, Ring A, Buschhaus B, Hirsch T, Daigeler A, Steinstraesser L, Steinau HU, Langer S. Influence of anti-inflammatory and vasoactive drugs on microcirculation and angiogenesis after burn in mice. Burns. 2011;37:656–664. - PubMed
-
- Corsetti G, Antona GD, Dioguardi FS, Rezzani R. Topical application of dressing with amino acids improves cutaneous wound healing in aged rats. Acta Histochem. 2010;112:497–507. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
