Cryoneurolysis: A Novel Treatment for Management of Spasticity. Presentation of a Case Series
- PMID: 40672642
- PMCID: PMC12264415
- DOI: 10.1177/27536351251340216
Cryoneurolysis: A Novel Treatment for Management of Spasticity. Presentation of a Case Series
Abstract
Background: Spasticity is a motor phenomenon occurring in disorders of the central nervous system that impacts on active and passive function, and quality of life. Pharmacological, physical and surgical management options are available, each of which have limitations. Cryoneurolysis is a technique developed for the treatment of pain which involves the controlled freezing and thawing of peripheral nerves. Recent case reports and series have suggested it may offer a novel treatment approach for pain associated with spasticity.
Objectives: To report on the evaluation of cryoneurolysis in the first cohort of patients treated in a UK spasticity clinic.
Methods: Eight patients with a variety of neurological conditions (aged 25-75 years) underwent cryoneurolysis. Each had been receiving regular botulinum toxin injections and had ongoing treatment goals. All patients first underwent diagnostic nerve blocks with local anaesthetic to determine their appropriateness for the treatment. Cryoneurolysis was then performed with ultrasound and nerve stimulator guidance. Assessments included goal attainment, Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS), ArmA, LegA and the patient reported impact of spasticity scale (PRISM), alongside patient satisfaction and side effect questionnaires. Assessments were at baseline and at regular intervals over 9 to 12 months.
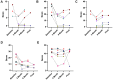
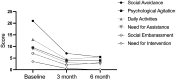
Results: All patients attained at least one of their goals, with sustained effect for more than 6 months. MAS demonstrated mixed or modest improvements. Functional outcome measures (ArmA/LegA) showed several meaningful improvements, particularly in passive function. There was an indication of an improvement in PRISM across domains, which plateaued at 6 months. Post-procedure pain was the most common side effect but subsided in all affected patients by 3 months. Patient satisfaction was positive.
Conclusions: Our findings contribute to a growing base of case reports and series suggesting that cryoneurolysis could be a potentially useful treatment modality for spasticity. Future controlled studies should aim to evaluate cost-effectiveness and compare with existing treatments.
Keywords: case reports; cryoneurolysis; goal attainment; neurological conditions; pain; spasticity.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article: AP has received honoraria from Ipsen and Merz. RD and MKF have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
