Development of high affinity antibodies to Plasmodium falciparum merozoite and sporozoite antigens during infancy and adulthood
- PMID: 40672955
- PMCID: PMC12263619
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1562671
Development of high affinity antibodies to Plasmodium falciparum merozoite and sporozoite antigens during infancy and adulthood
Abstract
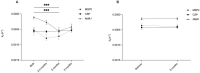
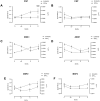
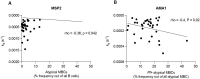
Antibodies are important for protection against malaria. For optimal protective activity, it is thought that antibodies need to have high affinity. A longitudinal study conducted in Uganda followed newborn infants and their mothers for nine months. The study found that antibody affinity (here measured as dissociation rate constant, kd) against the merozoite antigens AMA1 and MSP2 decreased from birth to six months in the infants, then gradually increased to 9 months, but not reaching the level observed in the mothers. In contrast, affinity against the sporozoite antigen CSP, did not change throughout the study period. Among mothers, no significant changes in antibody affinity were observed for any antigen, which is consistent with expectations for adults in an endemic area. Comparing specific antibody affinities to total antibody levels revealed almost no correlations, indicating that antibody magnitude and affinity evolve differently during immune development. Significant correlations were observed between antibody affinities and some atypical memory B cells. In conclusion, our study shows that development of naturally acquired slowly dissociating (high affinity) antibodies against malaria can evolve separately across different antigens. This is important information for future vaccine development studies.
Keywords: AMA1; CSP; MSP2; affinity; antibodies; falciparum; malaria.
Copyright © 2025 Lugaajju, Idro, Kiwuwa, Beeson, Drew, Mortazavi, Linse and Persson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . World Malaria Report 2024. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2024). Available at: https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/reports/world-malaria... (Accessed December, 2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

