[Live combined Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium improves glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetic mice with circadian rhythm disruption via the SCFAs/GPR43/GLP-1 pathway]
- PMID: 40673311
- PMCID: PMC12268902
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.15
[Live combined Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium improves glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetic mice with circadian rhythm disruption via the SCFAs/GPR43/GLP-1 pathway]
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the effects of live combined Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium (LCBE) on glucose and lipid metabolism in mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and circadian rhythm disorder (CRD) and explore the possible mechanisms.
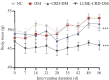
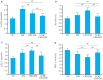
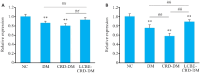
Methods: KM mice were randomized into normal diet (ND) group (n=8), high-fat diet (HFD) group (n=8), and rhythm-intervention with HFD group (n=16). After 8 weeks of feeding, the mice were given an intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (100 mg/kg) to induce T2DM. The mice in CRD-T2DM group were further randomized into two equal groups for treatment with LCBE (225 mg/kg) or saline by gavage; the mice in ND and HFD groups also received saline gavage for 8 weeks. Blood glucose level of the mice was measured using a glucometer, and serum levels of Bmal1, PER2, insulin, C-peptide and lipids were determined with ELISA. Colon morphology and hepatic lipid metabolism of the mice were examined using HE staining and Oil Red O staining, respectively, and fecal short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) was detected using LC-MS; GPR43 and GLP-1 expression levels were analyzed using RT-qPCR and Western blotting.
Results: Compared with those in CRD-T2DM group, the LCBE-treated mice exhibited significant body weight loss, lowered levels of PER2, insulin, C-peptide, total cholesterol (TC) and LDL-C, and increased levels of Bmal1 and HDL-C levels. LCBE treatment significantly increased SCFAs, upregulated GPR43 and GLP-1 expressions at both the mRNA and protein levels, and improved hepatic steatosis and colon histology.
Conclusions: LCBE ameliorates lipid metabolism disorder in CRD-T2DM mice by reducing body weight and improving lipid profiles and circadian regulators possibly via the SCFAs/GPR43/GLP-1 pathway.
目的: 分析枯草杆菌二联活菌肠溶胶囊(LCBE)对2型糖尿病合并昼夜节律紊乱糖脂代谢的影响以及作用机制。方法: 将KM小鼠随机分为3组,正常组8只,给予正常饲料喂养,高脂组8只,给予高脂饲料喂养,节律干预组16只,给予节律干预和高脂喂养,8 周后给予链脲佐菌素100 mg/kg腹腔注射,将节律干预糖尿病造模成功的小鼠随机分为2组,灌胃干预的2型糖尿病合并昼夜节律紊乱组(n=8)和2型糖尿病合并昼夜节律紊乱对照组(n=8),给予灌胃干预组225 mg/kg的LCBE灌胃干预,其余3组给予等体积的生理盐水,持续8 周。使用鱼跃血糖仪测小鼠血糖,ELISA法检测Bmal 1、PER 2、胰岛素、C肽和血脂水平,HE染色观察小鼠结肠变化,油红O染色观察对肝脏脂代谢的影响,液相色谱-质谱法检测粪便短链脂肪酸的水平,qPCR和Western blotting法检测小鼠GPR43和GLP-1基因及蛋白表达情况。结果: 与CRD-DM组比较,LCBE-CRD-DM组体质量、周期节律调节因子2(PER2)、胰岛素、C肽、T-CHO、TC和LDL-C水平明显下降(P<0.001),Bmal 1和HDL-C水平明显升高(P<0.001);灌胃干预后,LCBE-CRD-DM组短链脂肪酸、GPR43和GLP-1基因和蛋白表达水平明显高于CRD-DM组(P<0.001)。结论: LCBE能够降低节律紊乱2型糖尿病的体质量,改善小鼠的血脂水平,LCBE对节律紊乱2型糖尿病小鼠糖脂代谢的影响可能与SCFAs/GPR43/GLP-1通路有关。.
Keywords: circadian rhythm; glucolipid metabolism; live combined Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium; short-chain fatty acids; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








Similar articles
-
[Mechanism of Qingrun Decoction in alleviating hepatic insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic rats based on amino acid metabolism reprogramming pathways].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 Jun;50(12):3377-3388. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20250120.701. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40686115 Chinese.
-
Study on the modulation of kidney and liver function of rats with diabetic nephropathy by Huidouba through metabolomics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120136. Epub 2025 Jun 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40513925
-
Mulberry leaf improves type 2 diabetes in mice via gut microbiota-SCFAs-GPRs axis and AMPK signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:156970. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156970. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40527063
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 analogues for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 10;5(5):CD012204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28489279 Free PMC article.
-
Body weight and metabolic adverse effects of asenapine, iloperidone, lurasidone and paliperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis.CNS Drugs. 2012 Sep 1;26(9):733-59. doi: 10.2165/11634500-000000000-00000. CNS Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22900950
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
