Exploring Metal-Free Click Reactions: New Frontiers in Glycochemistry and Bioconjugation
- PMID: 40673383
- PMCID: PMC12371699
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5c00049
Exploring Metal-Free Click Reactions: New Frontiers in Glycochemistry and Bioconjugation
Abstract
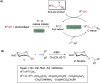
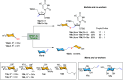
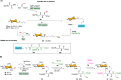
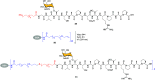
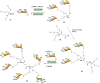
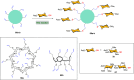
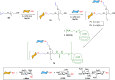
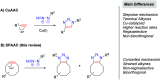
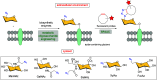
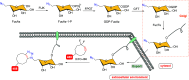
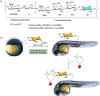
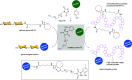
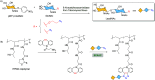
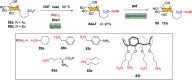
Efficient and biocompatible methods for synthesizing glycoconjugates are essential in chemical biology, as these molecules play pivotal roles in cellular recognition, signaling, and immune responses. Abnormal glycosylation is associated with diseases such as cancer, infections, and immune disorders, positioning glycoconjugates as promising candidates for therapeutic, diagnostic, and drug delivery applications. Traditional chemical approaches often lack biocompatibility and efficiency; however, the advent of metal-free click chemistry has revolutionized glycoconjugate synthesis by providing selective and versatile tools under mild conditions. This review highlights four remarkable metal-free click reactions: thiol-ene coupling (TEC), strain-promoted azide-alkyne cycloaddition (SPAAC), inverse electron-demand Diels-Alder (IEDDA) reaction, and sulfur fluoride exchange (SuFEx). TEC enables the regio- and stereoselective synthesis of glycoconjugates, including S-polysaccharides, glycopeptides, and glycoclusters, advancing vaccine development and carbohydrate-based therapeutics. SPAAC, a bioorthogonal and metal-free alternative, facilitates in vivo imaging, glycan monitoring, the synthesis of glycofullerenes and glycovaccines, and the development of targeted protein degradation systems such as lysosome-targeting chimeras (LYTACs). Additionally, the combination of SPAAC with biocatalysis offers a sustainable approach for preparing glycoconjugates with therapeutic potential. The IEDDA reaction, a highly efficient metal-free biorthogonal cycloaddition, plays a key role in metabolic glycoengineering for live-cell imaging and glycan-based therapies and also contributes to the creation of injectable hydrogels for drug delivery and tissue engineering. SuFEx, a more recent reaction, enables efficient sulfonamide and sulfonate bond formation, broadening the toolbox for glycoconjugate and protein functionalization. These methodologies are transforming glycochemistry and glycobiology, driving advancements in biomedicine, materials science, and pharmaceutical development.
Figures





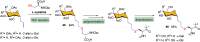














References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

