Carbohydrate-Rich Fraction of Aloe vera (L.) Burm.f. Extract Mitigates Bone Loss and Improves Metabolic Disturbance in Estrogen-Deficient Rats
- PMID: 40673869
- PMCID: PMC12269533
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.70148
Carbohydrate-Rich Fraction of Aloe vera (L.) Burm.f. Extract Mitigates Bone Loss and Improves Metabolic Disturbance in Estrogen-Deficient Rats
Abstract
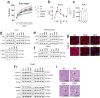
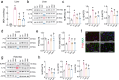
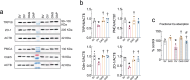
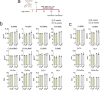
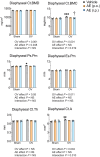
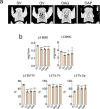
Aloe vera (L.) Burm.f., (AE) herb has been shown to have osteogenic, anti-diabetic, and prebiotic activities in animal and human studies. Postmenopausal women generally exhibit massive bone loss, impaired intestinal calcium absorption, obesity-related insulin resistance, and fat accumulation in the liver. It was possible that the AE herb may have a potential as a remedy for bone and metabolic disturbances associated with estrogen deficiency. Sham and ovariectomized rats were divided into 2 subgroups, that is, receiving daily administration of distilled water or 50 or 100 mg/kg of AE via either oral administration (p.o.) or intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) for 8 and 12 weeks. Nine weeks after ovariectomy, rats developed metabolic disturbances, as evidenced by obesity, impaired glucose tolerance, and high serum cholesterol levels. AE supplementation, either by p.o. or i.p., alleviated metabolic aberrations by improving glucose tolerance, reducing body weight, and decreasing fat deposition by increasing serum insulin levels. Furthermore, AE supplementation restored ovariectomy-associated calcium malabsorption to that of sham. At week 12 post-ovariectomy, massive bone loss was observed at trabecular-rich regions. Daily AE supplementation at 50 mg/kg for 12 weeks, but not 8 weeks, significantly increased BMD and BMC compared with those of sham. Additionally, AE enhanced bone formation and suppressed bone resorption, as shown by bone histomorphometry and serum bone turnover markers. These findings clearly demonstrated the anti-diabetic and osteogenic properties of Aloe vera extract in ovariectomized rats. Thus, Aloe vera had a potential as a nutraceutical candidate for the treatment of osteoporosis and metabolic disturbances associated with estrogen deficiency.
Keywords: anti‐diabetes; dyslipidemia; hyperglycemia; insulin resistance; osteogenesis; ovariectomy.
© 2025 The Author(s). Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007 Aug;(158):1-235. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007. PMID: 18088161 Free PMC article.
-
Citrullinemia Type I.2004 Jul 7 [updated 2022 Aug 18]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2004 Jul 7 [updated 2022 Aug 18]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301631 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Study on the modulation of kidney and liver function of rats with diabetic nephropathy by Huidouba through metabolomics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120136. Epub 2025 Jun 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40513925
-
Hormone replacement therapy to maintain cognitive function in women with dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(3):CD003799. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003799. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Jan 21;(1):CD003799. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003799.pub2. PMID: 12137718 Updated.
References
-
- Che C. T., George V., Ijinu T., Pushpangadan P., and Andrae‐Marobela K., “Traditional Medicine,” in Pharmacognosy (Elsevier, 2017), 15–30.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

