Aggressive B cell lymphomas retain ATR-dependent determinants of T cell exclusion from the germinal center dark zone
- PMID: 40674145
- PMCID: PMC12435852
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI187371
Aggressive B cell lymphomas retain ATR-dependent determinants of T cell exclusion from the germinal center dark zone
Abstract
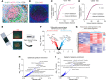
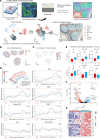
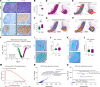
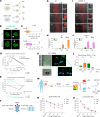
The germinal center (GC) dark zone (DZ) and light zone represent distinct anatomical regions in lymphoid tissue where B cell proliferation, immunoglobulin diversification, and selection are coordinated. Diffuse large B cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) with DZ-like gene expression profiles exhibit poor outcomes, though the reasons are unclear and are not directly related to proliferation. Physiological DZs exhibit an exclusion of T cells, prompting exploration of whether T cell paucity contributes to DZ-like DLBCL. We used spatial transcriptomic approaches to achieve higher resolution of T cell spatial heterogeneity in the GC and to derive potential pathways that underlie T cell exclusion. We showed that T cell exclusion from the DZ was linked to DNA damage response (DDR) and chromatin compaction molecular features characterizing the spatial DZ signature, and that these programs were independent of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) activity. As ATR is a key regulator of DDR, we tested its role in the T cell inhibitory DZ transcriptional imprint. ATR inhibition reversed not only the DZ transcriptional signature, but also DZ T cell exclusion in DZ-like DLBCL in vitro microfluidic models and in in vivo samples of murine lymphoid tissue. These findings highlight that ATR activity underpins a physiological scenario of immune silencing. ATR inhibition may reverse the immune-silent state and enhance T cell-based immunotherapy in aggressive lymphomas with GC DZ-like characteristics.
Keywords: Cell biology; Immunology; Lymphomas; Molecular pathology; Oncology; T cells.
Figures

Update of
-
Germinal Center Dark Zone harbors ATR-dependent determinants of T-cell exclusion that are also identified in aggressive lymphoma.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 18:rs.3.rs-4093618. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4093618/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: J Clin Invest. 2025 Jul 17;135(18):e187371. doi: 10.1172/JCI187371. PMID: 38562878 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

