Polyglycine-mediated aggregation of FAM98B disrupts tRNA processing in GGC repeat disorders
- PMID: 40674500
- PMCID: PMC12603922
- DOI: 10.1126/science.ado2403
Polyglycine-mediated aggregation of FAM98B disrupts tRNA processing in GGC repeat disorders
Abstract
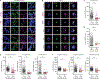
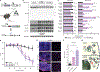
Aggregation-prone polyglycine-containing proteins produced from expanded GGC repeats are implicated in an emerging family of neurodegenerative disorders. In this study, we showed that polyglycine itself forms aggregates that incorporate endogenous glycine-rich proteins, including FAM98B, a component of the transfer RNA (tRNA) ligase complex (tRNA-LC) that harbors the most glycine-rich sequence in the human proteome. Through this glycine-rich intrinsically disordered region (IDR), polyglycine sequesters and depletes the tRNA-LC, disrupting tRNA processing. Accordingly, patient tissues revealed aggregate-associated FAM98B depletion and accumulation of aberrant tRNA splicing intermediates. Furthermore, Fam98b depletion in adult mice caused progressive motor coordination deficits and hindbrain pathology. Our data suggest that the FAM98B glycine-rich IDR mechanistically links previously disparate neurodegenerative disorders of protein aggregation and tRNA processing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Sutcliffe JS, Nelson DL, Zhang F, Pieretti M, Caskey CT, Saxe D, Warren ST, DNA methylation represses FMR-1 transcription in fragile X syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1, 397–400 (1992). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

