Cardiovascular Health Metrics, Genetic Susceptibility, and Incident Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Prospective Cohort Analysis
- PMID: 40675023
- PMCID: PMC12284668
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2025.102003
Cardiovascular Health Metrics, Genetic Susceptibility, and Incident Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Prospective Cohort Analysis
Abstract
Background: Evidence on the prospective relationship between cardiovascular health (CVH) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) risk is limited, particularly regarding genetic susceptibility as an effect modifier.
Objectives: We aimed to investigate the association between CVH levels and COPD risk and to determine whether genetic susceptibility influences this relationship.
Methods: We included 293,342 participants free of COPD from the UK Biobank cohort. CVH levels were assessed using the Life's Essential 8 (LE8) and the Life's Simple 7 scores. Genetic predisposition to COPD was quantified via the polygenic risk score. Cox proportional hazard models examined the impacts of CVH levels and polygenic risk score on COPD incidence.
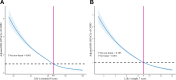
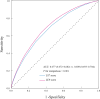
Results: During a median follow-up of 12.89 (Q1-Q3: 12.22-13.54) years, 9,481 participants developed COPD, with an incidence rate of 2.533 per 1,000 person-years (95% CI: 2.482-2.584). Compared to low CVH levels measured by LE8, the HRs (95% CI) for incident COPD were 0.468 (0.446-0.490) for moderate and 0.201 (0.177-0.227) for high CVH levels. No statistically significant interactions were observed between CVH levels and genetic susceptibility to COPD. LE8 showed better predictive accuracy for COPD incidence than Life's Simple 7, with a higher area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (0.698 [95% CI: 0.693-0.704] vs 0.677 [95% CI: 0.672-0.682], PDeLong < 0.001).
Conclusions: High CVH levels are significantly associated with a lower risk of incident COPD, regardless of genetic predisposition. These findings highlight the importance of maintaining optimal CVH in COPD prevention. (Predictors of coronary artery calcification [CAC] progression in the UKB population; 91090).
Keywords: Life's Essential 8; Life's Simple 7; cardiovascular health; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; polygenic risk score.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding support and author disclosures This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [82170457, 82200464, and 82371573] and the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation [2025A1515010683 and 2023A1515011730]. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, publication decision, or manuscript preparation. The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cumulative Life's Essential 8 Scores and Cardiovascular Disease Risk.JAMA Cardiol. 2025 Jul 1;10(7):649-656. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2025.0630. JAMA Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40266596 Free PMC article.
-
Life's Essential 8 scores, socioeconomic deprivation, genetic susceptibility, and new-onset chronic kidney diseases.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 Aug 5;138(15):1835-1842. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003491. Epub 2025 Apr 14. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 40223562 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of street-view greenspace exposure with cardiovascular health (Life's Essential 8) among women in midlife.Biol Sex Differ. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13293-025-00718-3. Biol Sex Differ. 2025. PMID: 40598663 Free PMC article.
-
Self-management interventions including action plans for exacerbations versus usual care in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 4;8(8):CD011682. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011682.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28777450 Free PMC article.
-
Computer and mobile technology interventions for self-management in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 23;5(5):CD011425. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011425.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28535331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christenson S.A., Smith B.M., Bafadhel M., Putcha N. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 2022;399(10342):2227–2242. - PubMed
-
- Zvezdin B., Milutinov S., Kojicic M., et al. A postmortem analysis of major causes of early death in patients hospitalized with COPD exacerbation. Chest. 2009;136(2):376–380. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

