Imaging high-frequency voltage dynamics in multiple neuron classes of behaving mammals
- PMID: 40675148
- PMCID: PMC12616578
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.06.028
Imaging high-frequency voltage dynamics in multiple neuron classes of behaving mammals
Erratum in
-
Imaging high-frequency voltage dynamics in multiple neuron classes of behaving mammals.Cell. 2025 Sep 4;188(18):5119. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.08.010. Epub 2025 Aug 21. Cell. 2025. PMID: 40845837 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
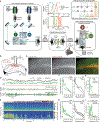
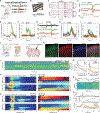
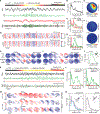
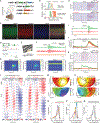
Fluorescent genetically encoded voltage indicators report transmembrane potentials of targeted cell types. However, voltage-imaging instrumentation has lacked the sensitivity to track spontaneous or evoked high-frequency voltage oscillations in neural populations. Here, we describe two complementary TEMPO (transmembrane electrical measurements performed optically) voltage-sensing technologies that capture neural oscillations up to ∼100 Hz. Fiber-optic TEMPO achieves ∼10-fold greater sensitivity than prior photometric voltage sensing, allows hour-long recordings, and monitors two neuron classes per fiber-optic probe in freely moving mice. With it, we uncovered cross-frequency-coupled theta- and gamma-range oscillations and characterized excitatory-inhibitory neural dynamics during hippocampal ripples and visual cortical processing. The TEMPO mesoscope images voltage activity in two cell classes across an ∼8-mm-wide field of view in head-fixed animals. In awake mice, it revealed sensory-evoked excitatory-inhibitory neural interactions and traveling gamma and 3-7 Hz waves in visual cortex and bidirectional propagation directions for both hippocampal theta and beta waves. These technologies have widespread applications probing diverse oscillations and neuron-type interactions in healthy and diseased brains.
Keywords: beta oscillations; fluorescence imaging; gamma oscillations; local field potentials; neural dynamics; sharp wave ripples; theta oscillations; voltage imaging; voltage indicators; voltage waves.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.J.S. is co-author of a U.S. patent, and S.H., R.C., and M.J.S. have pending patent applications related to the work in this paper.
Figures



Update of
-
Imaging high-frequency voltage dynamics in multiple neuron classes of behaving mammals.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 16:2024.08.15.607428. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.15.607428. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell. 2025 Aug 7;188(16):4401-4423.e31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.06.028. PMID: 39185175 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

