β-Hydroxybutyrate promotes cancer metastasis through β-hydroxybutyrylation-dependent stabilization of Snail
- PMID: 40675949
- PMCID: PMC12271565
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61541-3
β-Hydroxybutyrate promotes cancer metastasis through β-hydroxybutyrylation-dependent stabilization of Snail
Abstract
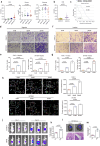
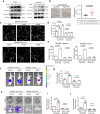
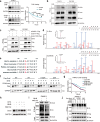
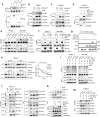
β-Hydroxybutyrylation (Kbhb) modification regulates protein molecular fates in either physiology or pathology, including cancer. However, the function and regulatory mechanism of Kbhb remain completely unknown in cancer metastasis. Here, we report that β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) is clinically associated with the progression of pancreatic cancer and functionally promotes pancreatic cancer cell metastasis. Mechanistically, BHB induces Kbhb modification of Snail at lysine 152 to enhance Snail stabilization, which is regulated by Kbhb modification enzyme CREB-binding protein (CBP), and subsequently prevents Snail degradation by blocking recognition of E3 ubiquitin ligases FBXL14. Furthermore, either targeting Snail Kbhb modification or CBP inhibitor decreases cancer metastasis and enhances the therapeutic efficacy of gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer cells. Collectively, our study reveals that Kbhb of Snail is critical to promote metastasis and provides a potential therapeutic strategy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

