Establishment of an interpretable MRI radiomics-based machine learning model capable of predicting axillary lymph node metastasis in invasive breast cancer
- PMID: 40676103
- PMCID: PMC12271558
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-10818-0
Establishment of an interpretable MRI radiomics-based machine learning model capable of predicting axillary lymph node metastasis in invasive breast cancer
Abstract
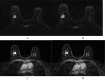
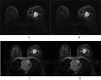
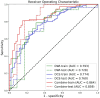
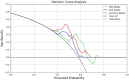
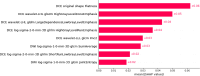
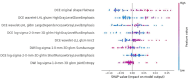
This study sought to develop a radiomics model capable of predicting axillary lymph node metastasis (ALNM) in patients with invasive breast cancer (IBC) based on dual-sequence magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and dynamic contrast enhancement (DCE) data. The interpretability of the resultant model was probed with the SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations) method. Established inclusion/exclusion criteria were used to retrospectively compile MRI and matching clinical data from 183 patients with pathologically confirmed IBC from our hospital evaluated between June 2021 and December 2023. All of these patients had undergone plain and enhanced MRI scans prior to treatment. These patients were separated according to their pathological biopsy results into those with ALNM (n = 107) and those without ALNM (n = 76). These patients were then randomized into training (n = 128) and testing (n = 55) cohorts at a 7:3 ratio. Optimal radiomics features were selected from the extracted data. The random forest method was used to establish three predictive models (DWI, DCE, and combined DWI + DCE sequence models). Area under the curve (AUC) values for receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were utilized to assess model performance. The DeLong test was utilized to compare model predictive efficacy. Model discrimination was assessed based on the integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) method. Decision curves revealed net clinical benefits for each of these models. The SHAP method was used to achieve the best model interpretability. Clinicopathological characteristics (age, menopausal status, molecular subtypes, and estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, and Ki-67 status) were comparable when comparing the ALNM and non-ALNM groups as well as the training and testing cohorts (P > 0.05). AUC values for the DWI, DCE, and combined models in the training cohort were 0.793, 0.774, and 0.864, respectively, with corresponding values of 0.728, 0.760, and 0.859 in the testing cohort. The predictive efficacy of the DWI and combined models was found to differ significantly according to the DeLong test, as did the predictive efficacy of the DCE and combined models in the training groups (P < 0.05), while no other significant differences were noted in model performance (P > 0.05). IDI results indicated that the combined model offered predictive power levels that were 13.5% (P < 0.05) and 10.2% (P < 0.05) higher than those for the respective DWI and DCE models. In a decision curve analysis, the combined model offered a net clinical benefit over the DCE model. The combined dual-sequence MRI-based radiomics model constructed herein and the supporting interpretability analyses can aid in the prediction of the ALNM status of IBC patients, helping to guide clinical decision-making in these cases.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Combined model; Lymph node metastasis; Magnetic resonance imaging; Radiomics; SHAP.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Multiparametric MRI Radiomics for Preoperative Prediction of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients With Invasive Breast Cancer: A Comparative Study.Cancer Innov. 2025 Jul 13;4(5):e70022. doi: 10.1002/cai2.70022. eCollection 2025 Oct. Cancer Innov. 2025. PMID: 40655318 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric MRI-based Interpretable Machine Learning Radiomics Model for Distinguishing Between Luminal and Non-luminal Tumors in Breast Cancer: A Multicenter Study.Acad Radiol. 2025 Jul;32(7):3801-3812. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2025.03.010. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40175203
-
A novel MRI-based radiomics for preoperative prediction of lymphovascular invasion in rectal cancer.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Aug;50(8):3377-3390. doi: 10.1007/s00261-025-04800-7. Epub 2025 Jan 12. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39799548
-
MRI-Based Radiomics Methods for Predicting Ki-67 Expression in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Acad Radiol. 2024 Mar;31(3):763-787. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.10.010. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Acad Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37925343
-
Positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the assessment of axillary lymph node metastases in early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Jan;15(4):iii-iv, 1-134. doi: 10.3310/hta15040. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 21276372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung, H. et al. Global Cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 Countries[J]. CA Cancer J. Clin.71 (3), 209–249. 10.3322/caac.21660 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

