LIMA1-alpha staining predicts curative intent surgery response in HPV negative head and neck cancer
- PMID: 40676267
- PMCID: PMC12340046
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-025-00266-8
LIMA1-alpha staining predicts curative intent surgery response in HPV negative head and neck cancer
Abstract
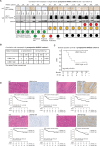
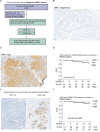
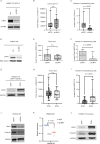
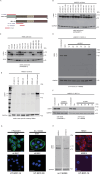
In many solid cancer types, surgery alone could be a sufficient first therapy option for a significant number of cancer patients. However, there are currently no diagnostic solutions to identify patients who could be stratified to surgery alone. To identify a biomarker predicting cancer surgery response, candidate biomarkers were studied in a non-metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (nmHNSCC) cohort well representative of the HPV-negative patient population. LIMA1 immunohistochemistry (IHC) with specificity-validated antibodies outperformed all other biomarkers in multivariable survival analyses of patients with nmHNSCC (n = 128, HR 2.10, P = 0.006). The prognostic effect was selective to LIMA1-alpha isoform IHC detection in patients who had received surgical therapy (n = 184, HR 2.39, P > 0.001). Strikingly, our real-world validation results, using two prospectively collected cohorts (n = 15 and n = 86), demonstrate that none of the LIMA1 negative patients died of HNSCC during the follow-up. Collectively, we report here the discovery of a diagnostic LIMA1-alpha IHC assay for HPV-negative HNSCC patient stratification to surgery-only therapy. Application of LIMA1 detection in routine nmHNSCC diagnostics would revolutionize the clinical management of HNSCC patients.
Keywords: Disease-Specific Survival; EPLIN; PV-TMA; Population-validated Tissue Microarray.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The University of Turku has filed a patent covering the diagnostic use of LIMA1 detection on behalf of SV and JW. SV and JW are co-founders and have an ownership interest in Thestra Ltd., developing LIMA1 IHC diagnostics for clinical use.
Figures




References
-
- Bozec A, Culié D, Poissonnet G, Dassonville O (2019) Current role of primary surgical treatment in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Curr Opin Oncol 31:138–145 - PubMed
-
- Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, Soulières D, Tahara M, de Castro G, Psyrri A, Basté N, Neupane P, Bratland Å (2019) Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 394:1915–1928 - PubMed
-
- Chow LQM (2020) Head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 382:60–72 - PubMed
-
- Gillison ML, Trotti AM, Harris J, Eisbruch A, Harari PM, Adelstein DJ, Jordan RCK, Zhao W, Sturgis EM, Burtness B (2019) Radiotherapy plus cetuximab or cisplatin in human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal cancer (NRG Oncology RTOG 1016): a randomised, multicentre, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 393:40–50 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

