Alignment between Duplex Sequencing and transgenic rodent mutation assay data in the assessment of in vivo NDMA-induced mutagenesis
- PMID: 40676325
- PMCID: PMC12454481
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-025-04121-0
Alignment between Duplex Sequencing and transgenic rodent mutation assay data in the assessment of in vivo NDMA-induced mutagenesis
Abstract
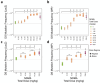
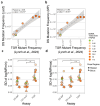
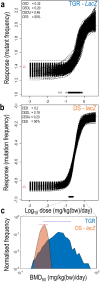
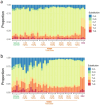
The nitrosamine N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) is a mutagen and rodent carcinogen that has been identified as a process impurity in some commercially available medicines, leading to market withdrawals and new impurity control measures. Error-corrected DNA sequencing techniques, such as Duplex Sequencing (DS), have error rates low enough to revolutionise genetic toxicology testing by directly measuring in vivo mutagenesis within days of exposure. Here, DS was performed on liver samples from an OECD-compliant, Transgenic Rodent Gene Mutation Assay (TGR) conducted under GLP standards. Muta™Mouse specimens were orally dosed with NDMA using either a repeat-dose 28-day regimen (0.02-4 mg/kg(bw)/day) or single bolus doses of either 5 or 10 mg/kg(bw) administered on day 1. Dose-dependent increases in mutation frequency were detected by DS in liver, enabling a No-Observed Genotoxic Effect Level (NOGEL) of 0.07 mg/kg(bw)/day to be determined, supported by mechanistic analyses of trinucleotide mutation spectra. Benchmark dose (BMD) modelling determined similar BMD50 values for both DS or TGR, demonstrating concordance across the two techniques albeit with greater precision from DS due to smaller inter-animal variation. DS offers a fundamental change in mutagenicity assessments enabling more precise point-of-departure determinations with mechanistic clarity and 3Rs advantages compared to the standard TGR approach.
Keywords: Benchmark dose; Error-corrected sequencing; Genetic toxicology; Nitrosamine; Non-clinical safety.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: AA, AD, FD and JE are employees of AstraZeneca and have shares in AstraZeneca. DN, JEH, JS, KV and TS were employed at TwinStrand Biosciences at the time the work was conducted and JEH, KV and TS have shares in TwinStrand Biosciences. JS is the founder, and has shares in, TwinStrand Biosciences and receives Duplex Sequencing Patent Royalties from the University of Washington. AL, JH and JW are employees of GSK and have shares in GSK. Ethics statement: All animal studies were ethically reviewed and carried out in accordance with Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 and the GSK Policy on the Care, Welfare and Treatment of Animals.
Figures


References
-
- Bercu JP, Zhang S, Sobol Z, Escobar PA, Van P, Schuler M (2023) Comparison of the transgenic rodent mutation assay, error corrected next generation duplex sequencing, and the alkaline comet assay to detect dose-related mutations following exposure to N-nitrosodiethylamine. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 891:503685. 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2023.503685 - PubMed
-
- Delker DA, Geter DR, Kleinert KM, Gollapudi BB (2008) Frequency and spectrum of lacI mutations in the liver of Big Blue mice following the administration of genotoxic carcinogens singly and in series. Int J Toxicol 27(1):35–42. 10.1080/10915810701876620 - PubMed
-
- Esina E, Dodge AE, Williams A et al (2024) Power analyses to inform Duplex Sequencing study designs for MutaMouse liver and bone marrow. Environ Mol Mutagen 65(8):234–242. 10.1002/em.22619 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

