Awareness and acceptability of long-acting injectable pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention among female students at tertiary learning institutions: a multi-center, institution-based cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40676534
- PMCID: PMC12269260
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-025-22271-9
Awareness and acceptability of long-acting injectable pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention among female students at tertiary learning institutions: a multi-center, institution-based cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Adolescent girls and young women (AGYW) in Zambia face an elevated risk of acquiring HIV. Long-acting injectable pre-exposure prophylaxis (LAI-PrEP) is an effective scientific method to prevent new HIV infections. However, awareness and acceptability of LAI-PrEP among AGYW remain limited. Thus, we aimed to assess awareness and acceptability of LAI-PrEP among female students.
Methods: This multi-center, institution-based cross-sectional study involved 760 female students from three universities in Lusaka, Zambia. Data were collected using a structured, self-administered questionnaire. Questions on acceptability and awareness were presented in a yes/no format. Data analysis was performed using STATA version 15.1.
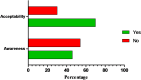
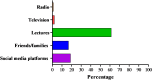
Results: Of the 760 participants, less than half, 349 (45.9%), were aware of injectable PrEP, with lectures being the most common source of information. In terms of acceptability, 531 (69.9%) of respondents indicated they would be willing to take LAI-PrEP once available. Biomedical science students were significantly less likely to accept injectable PrEP (AOR = 0.10, CI: 0.01-0.94, p = 0.044), as were those not at risk of HIV in the past three months (AOR = 0.41, CI: 0.21-0.81, p = 0.011). Conversely, knowing a partner's HIV status (AOR = 2.52, CI: 1.27-4.98, p = 0.0001) and being at risk of HIV in the past three months (AOR = 3.4, CI: 1.78-7.81, p = 0.011) were significantly associated with LAI-PrEP acceptability.
Conclusion: The study revealed a notable gap in awareness of LAI-PrEP among participants, with less than half being informed about its existence. Despite this low awareness, a significant majority expressed a willingness to accept LAI-PrEP if it were made available to them. This indicates a strong potential for adoption of LAI-PrEP, contingent upon improved education and awareness efforts.
Keywords: Acceptability; Awareness; HIV; Long-acting injectab; PrEP; Pre-exposure prophylaxis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The ethical approval of the study was obtained from the University of Zambia Health Science Research Committee (UNZAHSREC). All methods were carried out following relevant guidelines and regulations. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous