The application of super-resolution ultrasound radiomics models in predicting the failure of conservative treatment for ectopic pregnancy
- PMID: 40676578
- PMCID: PMC12269241
- DOI: 10.1186/s12958-025-01437-5
The application of super-resolution ultrasound radiomics models in predicting the failure of conservative treatment for ectopic pregnancy
Abstract
Background: Conservative treatment remains a viable option for selected patients with ectopic pregnancy (EP), but failure may lead to rupture and serious complications. Currently, serum β-hCG is the main predictor for treatment outcomes, yet its accuracy is limited. This study aimed to develop and validate a predictive model that integrates radiomic features derived from super-resolution (SR) ultrasound images with clinical biomarkers to improve risk stratification.
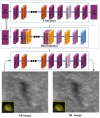
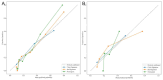
Methods: A total of 228 patients with EP receiving conservative treatment were retrospectively included, with 169 classified as treatment success and 59 as failure. SR images were generated using a deep learning-based generative adversarial network (GAN). Radiomic features were extracted from both normal-resolution (NR) and SR ultrasound images. Features with intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) ≥ 0.75 were retained after intra- and inter-observer evaluation. Feature selection involved statistical testing and Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression. Random forest algorithms were used to construct NR and SR models. A clinical model based on serum β-hCG was also developed. The Clin-SR model was constructed by fusing SR radiomics with β-hCG values. Model performance was evaluated using area under the curve (AUC), calibration, and decision curve analysis (DCA). An independent temporal validation cohort (n = 40; 20 failures, 20 successes) was used to validation of the nomogram derived from the Clin-SR model.
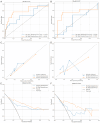
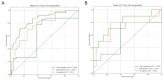
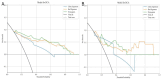
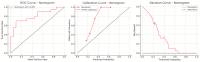
Results: The SR model significantly outperformed the NR model in the test cohort (AUC: 0.791 ± 0.015 vs. 0.629 ± 0.083). In a representative iteration, the Clin-SR fusion model achieved an AUC of 0.870 ± 0.015, with good calibration and net clinical benefit, suggesting reliable performance in predicting conservative treatment failure. In the independent validation cohort, the nomogram demonstrated good generalizability with an AUC of 0.808 and consistent calibration across risk thresholds. Key contributing radiomic features included Gray Level Variance and Voxel Volume, reflecting lesion heterogeneity and size.
Conclusions: The Clin-SR model, which integrates deep learning-enhanced SR ultrasound radiomics with serum β-hCG, offers a robust and non-invasive tool for predicting conservative treatment failure in ectopic pregnancy. This multimodal approach enhances early risk stratification and supports personalized clinical decision-making, potentially reducing overtreatment and emergency interventions.
Keywords: Conservative treatment failure prediction; Ectopic pregnancy; Machine learning; Radiomics; Super-resolution ultrasound.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Jinjiang Municipal Hospital (No. jjsyy2025-018-1.0). This is a retrospective study, with an exemption from obtaining signed informed consent from patients. All procedures followed the ethical standards of the responsible committees on human experimentation (institutional and national) and complied with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and its later amendments. Clinical trial number: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Development and validation of a machine learning model for predicting co-infection of Mycoplasma pneumonia in pediatric patients.Transl Pediatr. 2025 Jun 27;14(6):1201-1212. doi: 10.21037/tp-2024-562. Epub 2025 Jun 25. Transl Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40688218 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics Nomogram Based on Optimal Volume of Interest Derived from High-Resolution CT for Preoperative Prediction of IASLC Grading in Clinical IA Lung Adenocarcinomas: A Multi-Center, Large-Population Study.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241300734. doi: 10.1177/15330338241300734. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39569528 Free PMC article.
-
First trimester ultrasound tests alone or in combination with first trimester serum tests for Down's syndrome screening.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 15;3(3):CD012600. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012600. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28295158 Free PMC article.
-
First trimester serum tests for Down's syndrome screening.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 30;2015(11):CD011975. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011975. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26617074 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Super-Resolution Ultrasound Radiomics Can Predict the Upstaging of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ.Cancer Med. 2025 Aug;14(15):e71155. doi: 10.1002/cam4.71155. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40792423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeffers K, Koyfman A, Long B. Updates in emergency medicine: ectopic pregnancy[J]. Am J Emerg Med. 2024;85:90–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

