Biogenic Zinc nanoparticles: green approach to synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial applications
- PMID: 40676579
- PMCID: PMC12273035
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-025-02788-9
Biogenic Zinc nanoparticles: green approach to synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial applications
Abstract
Background: Biogenic synthesis of zinc nanoparticles (ZnNPs) has attracted significant interest due to their unique properties and potential biological applications. Unlike chemical and physical methods, biogenic synthesis offers a greener and more eco-friendly alternative. This study explores the synthesis of zinc-based nanoparticles using two distinct bacterial strains.
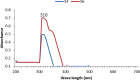
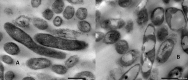
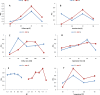
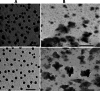
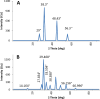
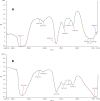
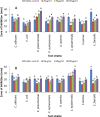
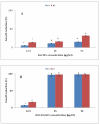
Results: In this study, zinc nanoparticles were synthesized in two forms: single-phase zinc sulfide nanoparticles (ZnS NPs) and mixed-phase zinc sulfide-oxide nanoparticles (ZnS-ZnO NPs), using Achromobacter sp. S4 and Pseudomonas sp. S6. The synthesis conditions were optimized for each strain, with pH playing a crucial role: Achromobacter sp. S4 favored basic conditions (pH 8.0) for zinc nanoparticles production, while Pseudomonas sp. S6 preferred acidic conditions (pH 4.7). TEM analysis revealed that Zn NPs from Pseudomonas sp. S6 were rod-shaped, whereas those from Achromobacter sp. S4 were spherical. Further characterization using EDX, XRD, and FTIR confirmed the successful synthesis of single phase ZnS NPs and hybride phase ZnS-ZnO NPs. Antimicrobial dose-response testing showed that single-phase ZnS NPs inhibited Klebsiella pneumoniae, while mixed-phase ZnS-ZnO NPs were effective against Staphylococcus epidermidis at 100 µg/ml based on inhibition zone measurements.Furthermore, the mixed-phase ZnS-ZnO NPs at 25 µg/ml demonstrated superior inhibition of microbial growth in sludge samples, likely due to a synergistic effect.
Conclusion: The study demonstrates the successful biogenic synthesis of ZnS NPs, and ZnS-ZnO NPs using two bacterial strains, with distinct morphological and functional properties. The use of two bacterial species was to assess strain-specific differences in nanoparticle synthesis and performance. The synthesized nanoparticles exhibited promising antimicrobial and environmental remediation potential, highlighting their applicability in both biomedical and environmental fields.
Keywords: Achromobacter sp.; Pseudomonas sp.; Biosynthesis; Microbial proliferation; Sludge remediation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Singh NA, Narang J, Garg D, Jain V, Payasi D, Suleman S, Swami RK. Nanoparticles synthesis via microorganisms and their prospective applications in agriculture. Plant Nano Biol. 2023;5:100047. 10.1016/j.plana.2023.100047. - DOI
-
- Irede EL, Awoyemi RF, Owolabi B, Aworinde OR, Kajola RO, Hazeez A, Raji AA, Ganiyu LO, Onukwuli CO, Onivefu AP, Ifijen IH. Cutting-edge developments in zinc oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and applications for enhanced antimicrobial and UV protection in healthcare solutions. RSC Adv 2024;14(29). https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2024/ra/d4ra02452d - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ammu VK, Pushpadass HA, Franklin MEE, Duraisamy R. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Carica papaya and Cymbopogon citratus leaf extracts: A comparative investigation of morphology and structures. J Mol Struct. 2025;1323:140737. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.140737. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

