Crosstalk between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α pathways in human islet models
- PMID: 40676831
- PMCID: PMC12279269
- DOI: 10.1080/19382014.2025.2526871
Crosstalk between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α pathways in human islet models
Abstract
Background: We previously showed that 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD - a persistent organic pollutant) activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) in pancreatic islets. The AHR is known to crosstalk with hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α) in other cell types but AHR-HIF1α crosstalk has not been previously examined in islet cells. Islet cell function is sensitive to hypoxia; we hypothesize that AHR activation by environmental pollutant(s) will interfere with the HIF1α pathway response in islets, which may be detrimental to islet cell function and survival during periods of hypoxia.
Methods: We assessed AHR-HIF1α crosstalk by treating human donor islets and stem cell-derived islets (SC-islets) with 10 nM TCDD ± 1% O2 and measuring gene expression of downstream targets of AHR (e.g. CYP1A1) and HIF1α (e.g. HMOX1).
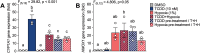
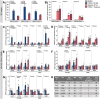
Results: In SC-islets, co-treatment with TCDD + hypoxia consistently suppressed CYP1A1 induction compared with TCDD treatment alone. In human islets, TCDD + hypoxia co-treatment suppressed CYP1A1 induction, but only in 2 of 6 donors. Both SC-islets and human donor islets displayed hypoxia-mediated suppression of glucose-6-phosphate catalytic subunit 2 (G6PC2) expression. Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) in human donor islets was impaired by hypoxia exposure, but unaffected by TCDD exposure.
Conclusion: Our study shows consistent AHR-HIF1α crosstalk in SC-islets and variable crosstalk in primary human islets, depending on the donor. In both cell models, hypoxia exposure interfered with activation of the AHR pathway by TCDD but there was no evidence that AHR activation interfered with the HIF1α pathway. In summary, our data show that co-exposure to an environmental pollutant and hypoxia results in molecular crosstalk in islets.
Keywords: CYP1A1; G6PC2; dioxin; human donor islets; hypoxia; stem cell-derived islets (SC-islets).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of an aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand on human trophoblast cell development.Hum Reprod. 2025 Jun 1;40(6):1163-1172. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaf075. Hum Reprod. 2025. PMID: 40294436
-
Hypoxia perturbs aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling and CYP1A1 expression induced by PCB 126 in human skin and liver-derived cell lines.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Feb 1;274(3):408-16. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24355420 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to the persistent organic pollutant 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD, dioxin) disrupts development of the zebrafish inner ear.Aquat Toxicol. 2023 Jun;259:106539. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2023.106539. Epub 2023 Apr 12. Aquat Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37086653 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas . 10th edition. www.diabetesatlas.org.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
