Comparative effectiveness of lifestyle interventions for prehypertension: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40677277
- PMCID: PMC12268206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpc.2025.101045
Comparative effectiveness of lifestyle interventions for prehypertension: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
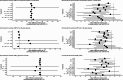
This study aims to compare the effectiveness of lifestyle interventions on systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) in individuals with prehypertension. A systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, and the Wanfang database from inception to December 2023. The analysis included randomized controlled trials with either parallel or cross-over designs. Utilizing a Bayesian network meta-analysis approach, we included 67 studies evaluating 17 lifestyle interventions compared with control. For SBP, dietary supplement plus exercise was the most effective lifestyle intervention, with a mean difference (MD) of -14.86 (95 % credible interval [CrI] -20.44 to -9.35). For DBP, health education plus meditation was the most effective lifestyle intervention (MD -13.99, 95 % CrI -22.25 to -5.65). Subgroup analyses showed that the effectiveness of the interventions varied by duration, age, and economic level of the region. This study underlines the importance of dietary factors and exercise in the management of prehypertension and highlights the superiority of multi-component lifestyle interventions. However, the effectiveness of these interventions varies based on participant characteristics and intervention type, emphasizing the need for tailored, population-specific approaches.
Keywords: Comparative effectiveness; Lifestyle intervention; Network meta-analysis; Prehypertension.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- WHO . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2023. Global report on hypertension: the race against a silent kille geneva: world health organization.https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240081062.10-14 [cited 2024 10-14] Available from:
-
- Unger T., Borghi C., Charchar F., Khan N.A., Poulter N.R., Prabhakaran D., et al. 2020 international society of hypertension global hypertension practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2020;75(6):1334–1357. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

