Acupuncture treatment preserves soleus muscle mass and improves mitochondrial function in a rat model of disuse atrophy
- PMID: 40677295
- PMCID: PMC12269403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imr.2025.101178
Acupuncture treatment preserves soleus muscle mass and improves mitochondrial function in a rat model of disuse atrophy
Abstract
Background: Muscle atrophy leads to debilitating loss of physical capacity, particularly when alternative treatments are needed. Acupuncture is proposed as a potential therapy for disuse atrophy, but its effects on muscle biology remain unclear. This study evaluated the effects of acupuncture on soleus muscle mass and mitochondrial function in a rat model of immobilization-induced atrophy.
Methods: Female Sprague Dawley rats were assigned to three groups: Control (CON), casting-induced immobilization (CT), and CT with acupuncture (CT-A) (n = 8). Immobilization of the left hindlimb lasted for 14 days, and acupuncture was performed at specific acupoints (stomach-36, gallbladder-34) three times per week for 15 min. Mitochondrial function was assessed in saponin-permeabilized fibers, and signaling molecules regulating muscle mass were analyzed by Western blot.
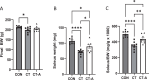
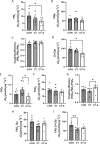
Results: CT-A attenuated soleus muscle atrophy compared to CT. Under fatty acid substrate conditions, CT reduced complex I and II-supported oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) compared to CON, while CT-A decreased respiratory leak and enhanced OXPHOS coupling relative to CT. Without fatty acids, CT-A decreased both respiratory leak and complex I and II-supported OXPHOS compared to CON, but differences between CT and CT-A were not significant. AMPKα activity (p-AMPKα/AMPKα) was significantly elevated in the CT group compared to the CON group, but returned to CON levels in the CT-A group. However, there were no changes in proteins associated with muscle atrophy or autophagy markers among the groups.
Conclusion: Acupuncture mitigates immobilization-induced muscle atrophy and preserves mitochondrial function, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic approach for muscle disuse conditions.
Keywords: Acupuncture; Immobilization; Mitochondrial respiration; Muscle atrophy.
© 2025 Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Zhang H., Qi G., Wang K., Yang J., Shen Y., Yang X., et al. Oxidative stress: roles in skeletal muscle atrophy. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;214 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

