An integrin-based quercetin 7-rhamnoside liver-targeted delivery liposomes for intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnancy
- PMID: 40677400
- PMCID: PMC12268842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102031
An integrin-based quercetin 7-rhamnoside liver-targeted delivery liposomes for intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnancy
Abstract
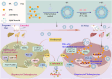
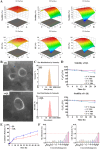
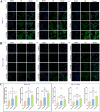
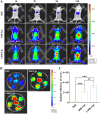
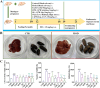
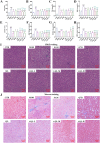
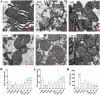
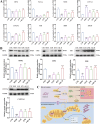
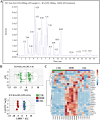
Intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnancy (ICP) is a characteristic disease during the perinatal period; however, its therapy remains unsatisfactory, and the pathogenesis remains unclear. The ameliorative effect of naturally occurring quercetin 7-rhamnoside (Q7R) in cholestasis has been established. In this study, we aimed to establish a nanoparticle-based peptide, A20FMDV2-modified liposome (t-QL), to encapsulate and deliver Q7R. Q7R bioavailability improved significantly when liposomes were used as carriers. This peptide A20FMDV2-modified nanosystem targeted integrin αvβ6 on biliary epithelial cells and improved stillbirth rates and liver function indicators better than free Q7R without a carrier. Q7R improved ICP by regulating mitochondrial function and bile metabolism. Our nanosystem provides a promising nanotherapeutic strategy for applying Q7R in ICP. We also elucidated a therapeutic mechanism underlying the action of ICP by simultaneously targeting mitochondrial structure and function, as well as bile acid metabolism.
Keywords: Bile acid metabolism; Intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnancy; Mitochondrial function; Nanodrug delivery system; Peptide A20FMDV2; Quercetin 7-rhamnoside.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Liu Y., Wei Y., Chen X., Huang S., Gu Y., Yang Z., et al. Genetic study of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in Chinese women unveils East Asian etiology linked to historic HBV epidemic. J. Hepatol. 2025;82:826–835. - PubMed
-
- Li J., Chen J., Lee P.M.Y., Zhang J., Li F., Ren T. Familial clustering of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: a nationwide population-based study in Denmark. Hepatology. 2023;78:389–396. Baltimore, Md. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

