Gold nanoparticle-loaded macrophages enhance radiotherapy via immune remodeling in oral cancer
- PMID: 40677404
- PMCID: PMC12268203
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102029
Gold nanoparticle-loaded macrophages enhance radiotherapy via immune remodeling in oral cancer
Abstract
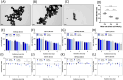
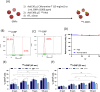
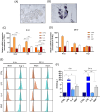
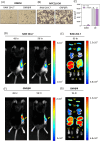
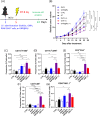
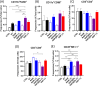
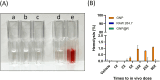
Gold nanoparticles (GNPs) are promising radiosensitizers owing to their high atomic number, but their therapeutic efficacy is often limited by reticuloendothelial system (RES)-mediated clearance and poor tumor accumulation attributable to elevated interstitial fluid pressure. This study explored macrophage-mediated GNP delivery to enhance radiotherapy (RT) efficacy in oral cancer by leveraging the tumor-homing ability, immune plasticity, hypoxia tropism, and RES evasiveness of macrophages. Murine oral cancer cells (MCTQ1) and macrophages (RAW 264.7) were used. GNPs were synthesized using the Turkevich method, which were then assessed for radiosensitization using cell viability and colony formation assays. GNPs were radiolabeled with Iodine-131 (131I) using the chloramine-T method, and uptake by RAW 264.7 cells was quantified at various time points to optimize the generation of GNP-loaded macrophages (GNP@Rs). MTCQ1 tumor-bearing mice were divided into control, RT, GNP, RAW, GNP + RT, RAW + RT, and GNP@R + RT groups. Tumor volumes were monitored after GNP or cell administration and/or RT (8 Gy). Flow cytometry was used to analyze the immune cell populations post-treatment. Transwell assays confirmed that GNP loading did not impair macrophage migration, and in vivo fluorescence imaging demonstrated strong tumor tropism of RAW 264.7 cells and GNP@Rs. GNP@Rs maintained their migration ability and exhibited robust tumor accumulation for up to 96 h. Notably, GNP@R + RT treatment significantly enhanced tumor suppression relative to RT alone and increased the infiltration of macrophages, activated dendritic cells, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and natural killer cells. Macrophage-mediated GNP delivery successfully improved RT outcomes in oral cancer by increasing radiosensitivity and modulating immune microenvironment.
Keywords: Gold nanoparticles; Immune response; Macrophage-based delivery; Radiosensitization; Radiotherapy.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Hui-Yen Chuang reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100007354Yen Tjing Ling Medical Foundation. Hui-Yen Chuang reports was provided by National Science and Technology Council. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Radiotherapeutic efficacy of gold nanoparticles for high dose-rate brachytherapy compared to conventional radiotherapy: An in vitro study.Med Phys. 2025 Jul;52(7):e18006. doi: 10.1002/mp.18006. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40665548 Free PMC article.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 6;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21735394
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated.
-
Oncolytic reovirus enhances the effect of CEA immunotherapy when combined with PD1-PDL1 inhibitor in a colorectal cancer model.Immunotherapy. 2025 Apr;17(6):425-435. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2025.2501926. Epub 2025 May 12. Immunotherapy. 2025. PMID: 40353308
-
Evaluating the theranostic potential of ferumoxytol when combined with radiotherapy in a mammary dual tumor mouse model.Med Phys. 2025 Jul;52(7):e17888. doi: 10.1002/mp.17888. Epub 2025 May 21. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40400098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Wahab M., et al. Radiotherapy and theranostics: a lancet oncology commission. Lancet Oncol. 2024;25(11):e545–e580. - PubMed
-
- Qiao Q., Li G. Inhibition of EGFR abrogates radioresistance in human oral cancer by inhibiting the endoplasmic reticulum stress chaperone GRP78. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018;102(3):E192. E192.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

