Clinical characteristics of patients with positive fungal pathogens during acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A retrospective study
- PMID: 40677416
- PMCID: PMC12266253
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pccm.2025.02.007
Clinical characteristics of patients with positive fungal pathogens during acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Fungal infections in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD) patients are poorly understood and often result in a poor prognosis. This study aimed to investigate the distribution of common fungi and the clinical features of AECOPD patients positive for fungal pathogens.
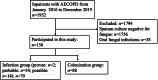
Methods: Data were collected from inpatients with AECOPD at the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University from January 2016 to December 2019. The enrolled patients were divided into an infection group and a colonization group, and clinical data were compared between the two groups. A 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) process was employed to ensure balanced samples to analyze the impact of positive fungal pathogens on the clinical features of AECOPD patients. The incidence of acute exacerbations one year after discharge was determined via telephone follow-up.
Results: The most frequently isolated fungal pathogen was Candida albicans (164/395, 41.5 %), followed by Aspergillus (93/395, 23.5 %). After propensity score matching, 68 patients were equally divided into the infection and colonization groups. There was no significant difference in clinical manifestations between the infection and colonization groups (P > 0.05). Patients in the infection group had significantly higher procalcitonin (PCT) values (0.2 [0.1, 0.7] ng/ml vs. 0.1 [0, 0.1] ng/ml; P = 0.003) and lower albumin/globulin ratios (1.1 [0.6, 1.3] vs. 1.1 [1.0, 1.3], P = 0.047) than those in the colonization group. The antibiotic treatment (12.5 [11.0, 19.0] days vs. 10.0 [8.0, 14.0] days; P = 0.002) and hospitalisation duration (18.0 [14.7, 22.5] days vs. 11.0 [8.0, 16.0] days; P < 0.001) in the infection group was significantly longer than that in the colonization group. In addition, more patients in the colonization group received non-invasive mechanical ventilation (76.5 % [26/34] vs. 47.1 % [16/34]; P = 0.013). Compared with the colonization group, more patients in the infection group underwent bronchoscopy (29.4 % [10/34] vs. 2.9 % [1/34]; P = 0.003). Using multivariable analysis, we found that bronchoscopy (OR: 1.350, 95 % CI: 1.020-1.771, P = 0.034) and duration of antibiotics used (OR: 1.318, 95 % CI: 1.090-1.560, P = 0.004) were risk factors for pulmonary fungal infection in AECOPD patients.
Conclusion: Candida albicans and Aspergillus are the common fungi isolated from patients with AECOPD. The clinical manifestations of AECOPD patients with fungal infection are nonspecific. AECOPD patients with positive fungal isolation who have undergone bronchoscopy and used antibiotics for a longer duration are more likely to have fungal infection.
Keywords: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Colonization; Fungal pathogen; Infection; Risk factor.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Self-management interventions including action plans for exacerbations versus usual care in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 4;8(8):CD011682. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011682.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28777450 Free PMC article.
-
Sputum colour charts to guide antibiotic self-treatment of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the Colour-COPD RCT.Health Technol Assess. 2025 May;29(28):1-42. doi: 10.3310/KPFD5558. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40418146 Clinical Trial.
-
Immunostimulants versus placebo for preventing exacerbations in adults with chronic bronchitis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 14;11(11):CD013343. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013343.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36373977 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive ventilation for the management of acute hypercapnic respiratory failure due to exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 13;7(7):CD004104. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004104.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28702957 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic antibiotics for adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jan 15;1(1):CD013198. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013198.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33448349 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

