Effect of Blood Pressure Control on Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40677434
- PMCID: PMC12270503
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.86230
Effect of Blood Pressure Control on Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review
Abstract
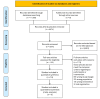
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), with hypertension, common in this population, contributing significantly to vascular damage and cardiovascular risk. This systematic review evaluates the impact of blood pressure (BP) control on cardiovascular outcomes in individuals with CKD. A comprehensive search of PubMed, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Scopus, and Web of Science up to May 5, 2025, identified randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and prospective comparative studies assessing BP interventions and cardiovascular outcomes in CKD populations. Methodological quality was appraised using the Modified Downs and Black checklist. Of the 11,606 studies screened, 10 met the inclusion criteria. Interventions included intensive BP targets, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) blockers, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, and antioxidant therapies. Most studies reported significant reductions in cardiovascular events, particularly with intensive BP control, though risks such as acute kidney injury (AKI) and hyperkalemia were noted. Nutraceuticals showed potential for anti-inflammatory and BP-lowering benefits. Overall, the methodological quality was high, with most studies rated as good to excellent. Targeted BP control appears to significantly reduce cardiovascular risk in CKD patients; however, individualized treatment strategies are essential to minimize adverse renal outcomes. While the evidence supports the cardiovascular benefits of BP management in this population, further research is needed to optimize intervention strategies and define safety thresholds.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; antioxidant therapy; blood pressure control; cardiovascular disease; cardiovascular outcomes; chronic kidney disease; hypertension; nutraceuticals; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockers; sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitors.
Copyright © 2025, Ahmed et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998;32:0–9. - PubMed
-
- Hypertension in CKD: core curriculum 2019. Ku E, Lee BJ, Wei J, Weir MR. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019;74:120–131. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous