Familial Hypercholesterolemia Mimicking Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Rare Case From Pakistan
- PMID: 40677462
- PMCID: PMC12270350
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.86207
Familial Hypercholesterolemia Mimicking Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Rare Case From Pakistan
Abstract
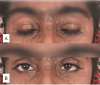
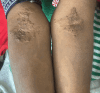
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetically inherited lipid disorder characterized by markedly elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), leading to premature cardiovascular disease and distinctive cutaneous manifestations such as tendon xanthomas and corneal arcus. We present the case of a young Pakistani woman with extensive yellowish plaques over her chest, hands, feet, and periocular area, alongside progressive deformities of the fingers and toes that clinically resembled rheumatoid arthritis, which developed over the course of four years. Laboratory investigations revealed significantly elevated total and LDL cholesterol, while autoimmune markers including rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-CCP were negative. Radiographic imaging demonstrated soft tissue swelling, reduced joint spaces, and features of acro-osteolysis in the affected digits, suggestive of xanthomatous infiltration. The diagnosis of FH was established using clinical criteria, including the Simon-Broome criteria, Dutch Lipid Clinic Network (DLCN), and MEDPED scores, in the absence of genetic testing due to limited access. The patient was initiated on high-dose statin therapy with dietary and lifestyle modifications, and parents were offered genetic counselling. Although Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors (PCSK9) therapy was considered, its availability and cost posed significant barriers. This case highlights the critical role of physical findings and diagnostic scoring tools in identifying FH in resource-limited settings and adds to the scarce literature by reporting a rare rheumatoid-like presentation of FH, the first of its kind from Pakistan.
Keywords: corneal arcus; familial hypercholestrolemia; rheumatoid arthritis; seronegative rheumatoid arthritis; tendon xanthoma.
Copyright © 2025, Golani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Elucigene FH20 and LIPOchip for the diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2012;16(17):1-266. doi: 10.3310/hta16170. Health Technol Assess. 2012. PMID: 22469073 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of PCSK9 Inhibitors Alirocumab and Evolocumab.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016 Jun;22(6):641-653q. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2016.22.6.641. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27231792 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical scores fail to sufficiently identify children with Familial Hypercholesterolemia.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2025 Jul 9:zwaf301. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwaf301. Online ahead of print. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40632909
-
Proposal of a Familial Hypercholesterolemia Pediatric Diagnostic Score (FH-PeDS).Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2025 Jun 20:zwaf352. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwaf352. Online ahead of print. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40578816
-
Efficacy and Safety of Inclisiran in Adolescents With Genetically Confirmed Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Results From the Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Part of the ORION-13 Randomized Trial.Circulation. 2025 Jun 24;151(25):1758-1766. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.073233. Epub 2025 May 20. Circulation. 2025. PMID: 40391436 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Complex coronary artery lesions in a young woman with an acute myocardial infarction and genetically confirmed familial hypercholesterolemia: a case report and literature review from a developing country. Nguyen KM, Hoang SV, Nguyen TN, Ly SQ, Dang VT, Ly TI, N Tran HP. Cureus. 2024;16:0. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Worldwide prevalence of familial hypercholesterolemia: meta-analyses of 11 million subjects. Beheshti SO, Madsen CM, Varbo A, Nordestgaard BG. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:2553–2566. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
