Effect of Yoga on Pulmonary Function Tests and Arterial Stiffness in Post-COVID-19 Mild Moderate Cases
- PMID: 40677675
- PMCID: PMC12123502
- DOI: 10.26574/maedica.2025.20.1.48
Effect of Yoga on Pulmonary Function Tests and Arterial Stiffness in Post-COVID-19 Mild Moderate Cases
Abstract
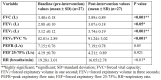
Background: COVID-19 caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 has resulted in significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. Long term respiratory complications secondary to COVID-19 have been described, which were not fully explored. The severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) directly infects endothelial cells, with inducing marked endothelial damage and inflammation contributing to increased arterial stiffness. Yoga is a holistic psychosomatic approach that leads to improvement of pulmonary and cardiovascular functions. Hence, this study aimed to evaluate the effect of yoga on pulmonary functions and arterial stiffness who have suffered from COVID-19. Objectives: The aim of the present interventional study was to measure and investigate the effect of yoga on the pulmonary function tests and arterial stiffness in post-COVID-19 mild and moderate cases. Material and method:After taking the approval of the Institutional Ethical Committee (IEC), 30 post-COVID-19 patients were recruited into the study. The baseline arterial stiffness (oscillometric method) and baseline pulmonary functions tests were assessed (using computerized spirometer HELIOS 70). The study participants were then subjected to a yoga intervention for eight weeks. Pulmonary function tests and arterial stiffness was assessed after the yoga intervention and findings were compared with the baseline data. Results:After eight weeks of yoga intervention, there was a statistically significant increase in the mean values of FEV1, FEV3, FVC and percentage of FEV1/FVC ratio (p<0.05), and a highly significant decrease in two arterial stiffness parameters, including brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) (p<0.001) and carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV) (p<0.001). This shows that performing yoga regularly has a significant effect on the body vasculature and arterial stiffness. Pearson correlation test showed a positive correlation between systolic blood pressure (SBP) and baPWV (r=0.45) (p<0.001). There was also a positive correlation observed between cfPWV (r=0.37) and systolic blood pressure (SBP) (p<0.05). Conclusions:The study indicates that pulmonary function tests and arterial stiffness improve in post-COVID-19 mild and moderate cases with eight weeks of regular yoga practice.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures





References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO director general’s remarks at the media briefing on 2019-nCo-V on 11 Feb 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-remarks-at.... Lancet Respir Med.
-
- Zieman SJ, Melenovsky V, Kass DA. Mechanisms, pathophysiology and therapy of arterial stiffness. Arter Thromb Vasc Biol . 2005;25:932–943. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
