Molecular crosstalk in SP7-mediated osteogenesis: Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential
- PMID: 40677780
- PMCID: PMC12266214
- DOI: 10.1016/j.afos.2025.04.003
Molecular crosstalk in SP7-mediated osteogenesis: Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential
Abstract
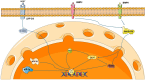
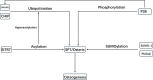
SP7, also known as Osterix, is a zinc finger-containing transcription factor, plays a crucial role in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. This review examines the molecular mechanisms underlying SP7's regulatory functions, highlighting its interactions with key signaling pathways such as BMP-SMAD, Wnt/β-catenin, and HIF-1α. SP7 acts downstream of RUNX2 to regulate osteogenic gene expression, including collagen Type I Alpha 1 (COL1A1), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and osteocalcin (OCN). The review also explores the role of post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation and ubiquitination, in modulating SP7's stability and activity. Emerging therapeutic strategies targeting SP7, including gene editing, RNA-based approaches, and small-molecule modulators, are discussed as innovative solutions for treating osteoporosis and other skeletal disorders. The potential for future research into SP7's interactions with non-coding RNAs and angiogenesis pathways is emphasized, underscoring its significance in skeletal health and regenerative medicine. This comprehensive overview consolidates current knowledge of SP7's molecular functions, therapeutic potential, and its pivotal role in bone biology.
Keywords: BMP; HIF-1α; Osteogenesis; Osteoporosis; SOST; SP7.
© 2025 The Korean Society of Osteoporosis. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Nakashima K., Zhou X., Kunkel G., Zhang Z., Deng J.M., Behringer R.R., et al. The novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell. 2002;108:17–29. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

