Bowel perforation and partial volvulus associated with erosion of inflatable penile prosthesis
- PMID: 40677938
- PMCID: PMC12268694
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eucr.2025.103093
Bowel perforation and partial volvulus associated with erosion of inflatable penile prosthesis
Abstract
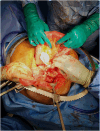
Erosion of the reservoir is a rare complication of inflatable penile prosthesis (IPP) placement. We emphasize maintaining a broad differential in patients with abdominal pain and a history of IPP. We present a 61-year-old male with abdominal pain, imaging showing abnormal mesenteric swirling, loculated fluid suggestive of a ruptured appendix in an internal hernia, and an associated foreign body. He underwent diagnostic laparoscopy, then exploratory laparotomy, revealing partially volvulated small bowel and colon around the penile reservoir. Consider implant erosion in similar presentations. Submuscular placement may reduce bowel complication risks.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

