Higher Pre-Operative Non-Invasive Fibrosis Scores are not Associated with Surgical Outcomes in Patients with MASLD Undergoing Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery
- PMID: 40677984
- PMCID: PMC12269317
- DOI: 10.3138/canlivj-2024-0015
Higher Pre-Operative Non-Invasive Fibrosis Scores are not Associated with Surgical Outcomes in Patients with MASLD Undergoing Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery
Abstract
Background: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a leading cause of cirrhosis in Canada. Metabolic and bariatric surgery (MBS) leads to histologic improvement in patients with MASLD and obesity; however, patients with advanced fibrosis may be at risk for decompensation in liver function following MBS. There are currently no Canadian data evaluating the association between pre-operative advanced fibrosis and post-operative complications among patients with obesity undergoing MBS.
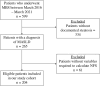
Methods: We conducted a single-centre retrospective cohort study of individuals undergoing primary MBS (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy) between September 2016 and August 2021. The primary exposure was pre-operative NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) fibrosis score (NFS). Outcomes of interest included post-operative complications and health care utilization at 30 and 90 days, and weight loss at 30 days post-operatively.
Results: After exclusions, 204 patients who received MBS and had the data required to calculate NFS were included. The median age was 46 years (interquartile range 38-55 years) and 181 (89%) were female. A total of 55 (27%) patients had NFS, suggesting advanced fibrosis. There was no significant difference in 30- or 90-day complications and health care utilization rates in patients with higher NFS.
Conclusions: Patients undergoing MBS have a high prevalence of steatosis and advanced fibrosis based on the NFS. Our data suggest that higher NFS is not associated with higher short-term post-operative complications in patients undergoing MBS. Further work needs to be done to determine the optimal method of screening for advanced liver disease in patients living with severe obesity.
Keywords: NAFLD fibrosis score; advanced; liver; metabolic and bariatric surgery; metabolic associated steatotic liver disease; patients.
Plain language summary
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is the leading cause of cirrhosis in Canada. Metabolic and bariatric surgery (MBS) can help treat MASLD by reducing the amount of fat and scarring in the liver. However, some patients with MASLD can experience worsening of their liver function after surgery. While liver biopsies remain the gold standard for diagnosing MASLD and grading its severity, they are also invasive and have risks associated with them. Non-invasive tests like the NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) fibrosis score (NFS), which use a combination of bloodwork and patient demographics, can be used to screen for advanced liver scarring in patients with MASLD. Our study aimed to determine how common advanced scarring was in patients undergoing MBS, and whether a higher NFS was associated with worse outcomes after surgery. Using the NFS, we discovered that over 25% of patients with MASLD undergoing MBS have advanced scarring; however, patients with higher NFS did not have more complications after surgery. Future studies should continue exploring the best methods of screening for MASLD and advanced scarring in patients living with obesity to determine who is at higher risk for complications after MBS.
© Canadian Association for the Study of the Liver, 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
N/A
References
-
- Verrastro O, Panunzi S, Castagneto-Gissey L, et al. Bariatric-metabolic surgery versus lifestyle intervention plus best medical care in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (BRAVES): a multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet. 2023;401:1786–97. 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00634-7. Medline: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials