Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy for advanced HPV-related penile squamous cell carcinoma: a rare case report
- PMID: 40678061
- PMCID: PMC12266999
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1569124
Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy for advanced HPV-related penile squamous cell carcinoma: a rare case report
Abstract
Background: Human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV-16)-associated penile squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC) poses considerable therapeutic challenges, especially in its advanced stages. Although surgery continues to be the cornerstone of treatment, immunotherapeutic approaches hold a promising alternative for patients unable to endure conventional chemotherapy.
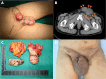
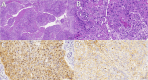
Case summary: A 69-year-old male presented with progressive ulceration of the foreskin over the course of one year, which ultimately extended to the glans, accompanied by inguinal lymph node metastasis. The patient underwent surgical resection, including bilateral inguinal lymph node dissection. Histopathological examination confirmed a diagnosis of HPV-16-related PSCC with concomitant PD-L1 expression. Given the patient's poor tolerance to chemotherapy, he was treated with four cycles of the PD-1 inhibitor tislelizumab, resulting in a partial response.
Conclusion: This case underscores the promising potential of immunotherapy as a viable alternative treatment for advanced PSCC in patients who are unable to tolerate chemotherapy. The synergistic integration of surgical intervention, immunotherapy, and psychological support is essential to achieving the best possible outcomes for patients.
Keywords: advanced cancer; checkpoint inhibitors; human papillomavirus type 16; immunotherapy; lymph node dissection; penile squamous cell carcinoma.
Copyright © 2025 Pan, Wu, Shi and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

