The role of Lobectomy in Glioblastoma management: A Retrospective series
- PMID: 40678087
- PMCID: PMC12269866
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bas.2025.104305
The role of Lobectomy in Glioblastoma management: A Retrospective series
Abstract
Introduction: Treatment choices for glioblastoma (GB) remain scarce. Multiple clinical studies have demonstrated the importance of supramaximal resection. Recently, it is emphasized the efficacy of lobectomy as treatment option in GB patients, achieving the maximum overall survival (OS) and progression free survival (PFS).
Research question: The primary aim of this study is to assess the OS and PFS of GB patients undergoing lobectomy, compared to those undergoing lesionectomy. Secondary aims include the identification of potential survival modifiers among clinical parameters.
Materials and methods: This retrospective analysis consists of a multicenter case series of GB patients who underwent lobectomy or lesionectomy between January 2015 and December 2022. Primary outcome included OS and PFS. Identification of potential survival modifiers and postoperative complications were also recorded. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were generated to assess overall survival. Multivariate analyses were performed to identify factors associated with survival.
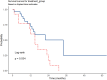
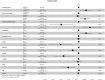
Results: This study included 43 patients. There were 29 cases of lobectomy and 14 cases of lesionectomy. The median OS in lobectomy group was 34 months, compared to 15 months in the lesionectomy group. Multivariate regression analysis indicated that advanced age, tumor location, neurological deficits and the performance of lesionectomy were associated with poorer survival outcomes.
Discussion and conclusions: Lobectomy in GB cases is associated with increased OS, compared to lesionectomy. In our series, we demonstrated a significantly better survival with lobectomy than lesionectomy. However, there are complications associated with lobectomy. The identification of the subgroup of patients who would benefit from a lobectomy needs to be addressed.
Keywords: Glioblastoma; Lobectomy; Overall survival; Progression-free survival; Retrospective.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Treatment options for progression or recurrence of glioblastoma: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 4;5(1):CD013579. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013579.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34559423 Free PMC article.
-
Optimisation of chemotherapy and radiotherapy for untreated Hodgkin lymphoma patients with respect to second malignant neoplasms, overall and progression-free survival: individual participant data analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 13;9(9):CD008814. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008814.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28901021 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Comparison of first-line chemotherapy including escalated BEACOPP versus chemotherapy including ABVD for people with early unfavourable or advanced stage Hodgkin lymphoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 25;5(5):CD007941. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007941.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28541603 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
References
-
- Borger V., Hamed M., Ilic I., Potthoff A.-L., Racz A., Schäfer N., Güresir E., Surges R., Herrlinger U., Vatter H., Schneider M., Schuss P. Seizure outcome in temporal glioblastoma surgery: lobectomy as a supratotal resection regime outclasses conventional gross-total resection. J. Neuro Oncol. 2021;152(2):339–346. doi: 10.1007/s11060-021-03705-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

