Bibliometric Analysis of Craving in Drug and Behavioral Addiction During the Last Decade
- PMID: 40678103
- PMCID: PMC12265440
- DOI: 10.32598/bcn.2023.194.6
Bibliometric Analysis of Craving in Drug and Behavioral Addiction During the Last Decade
Abstract
Introduction: According to the review studies, the growing knowledge of craving and the relevant causal factors that have led to the accumulation of solid theoretical frameworks over the past few years make it necessary to carry out a bibliometric review of this literature.
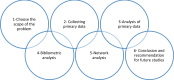
Methods: In this study, by examining the papers published during the last decade in the Scopus database, the largest citation database functional in mapping and content analysis of citation data, the researchers tried to clarify the research direction in the coming years.
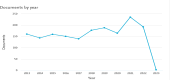
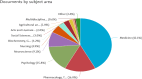
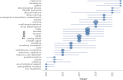
Results: In craving research, multi-authored articles, such as Boswell's (2016) study, garnered the highest number of citations. Boswell (2016) and Wolff (2016) have emerged as prominent figures in this field. Li X and the journal of addictive behaviors are leading producers of research in the craving domain. The highest volume of scientific output originates from the Department of Psychiatry, Yale University School of Medicine, with significant contributions from the United States, China, Germany, Italy, and England. The term "craving" exhibits the highest frequency of use. The co-authorship network illustrates that the most significant collaborations occur between the United States and other countries, where the majority of scientific output in this field is concentrated.
Conclusion: This analysis leads to the conclusion that studies about cravings occupy a prominent position in global etiological research and therapeutic interventions for addictive disorders. The enduring popularity of authors and publications addressing these disorders remains noteworthy.
Keywords: Addictive behaviors; Bibliography; Craving; Drug addiction.
Copyright© 2025 Iranian Neuroscience Society.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Research status, hotspots and perspectives of artificial intelligence applied to pain management: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Updates Surg. 2025 Jun 28. doi: 10.1007/s13304-025-02296-w. Online ahead of print. Updates Surg. 2025. PMID: 40580377
-
Knowledge graph and bibliometric analysis of inflammatory indicators in ovarian cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 30;15:1533537. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1533537. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40661780 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Global Analysis of Future Trends in Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Veterinary Medicine.Vet Med Sci. 2025 May;11(3):e70258. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70258. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40145983 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Driving innovations in cancer research through spatial metabolomics: a bibliometric review of trends and hotspot.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 10;16:1589943. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1589943. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40557160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albarracín M. L. G., Castro C. M., Chaparro P. E. (2020). Importance, definition and conflicts of authorship in scientific publications. Revista Bioética, 28(1), 10–16. [DOI: 10.1590/1983-80422020281361] - DOI
-
- Babaii E., Taase Y. (2013). Author-assigned keywords in research articles: Where do they come from. Iranian Journal of Applied Linguistics, 16(2), 1–19. [https://ijal.khu.ac.ir/article-1-1786-fa.pdf]
-
- Candel G., Naccache D. (2021). Generating local maps of science using deep bibliographic coupling [Preprint]. arXiv. [DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2109.10007] - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
