Interventional approaches to combat obesity: Exploring the metabolomic signature of weight loss trials
- PMID: 40678167
- PMCID: PMC12269453
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metop.2025.100373
Interventional approaches to combat obesity: Exploring the metabolomic signature of weight loss trials
Abstract
Obesity is characterized by the expansion of adipose tissue, contributing to systemic low-grade inflammation, insulin resistance, and widespread disruption of metabolic pathways. These pathophysiological changes are strongly linked to the development of several chronic conditions, including metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain forms of cancer. Metabolomics have emerged as a powerful analytical approach for elucidating obesity-related metabolic disturbances at both the cellular and systemic levels, enabling the identification of specific metabolic signatures associated with disease risk and progression. This narrative review synthesizes findings from interventional weight loss studies that addressed obesity using various strategies, including dietary modification, physical activity, pharmacotherapy, and bariatric surgery. Focusing on studies employing metabolomic techniques, this review highlights both consistent and divergent patterns in metabolite changes observed following weight loss, particularly in the metabolism of amino acids, lipids, short-chain fatty acids, and other metabolic pathways affected by each intervention. These insights have the potential to inform the development of more personalized and effective therapeutic approaches for obesity, thereby advancing the implementation of precision medicine in obesity management.
Keywords: Amino acids; Bariatric surgery; Lipids; Metabolism; Physical exercise; Short-chain fatty acids; Weight loss.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Given her role as co Editor in chief, Maria Dalamaga had no involvement in the peer review of this article and had no access to information regarding its peer review. Full responsibility for the editorial process for this article was delegated to another journal editor If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

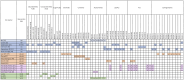

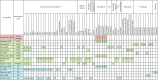
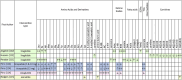
References
-
- Panuganti K.K., Nguyen M., Kshirsagar R.K. StatPearls Publishing; 2025. Obesity.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459357/ - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO), Obesity and overweight, (n.d.). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed May 14, 2025).
-
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. Afshin A., Forouzanfar M.H., Reitsma M.B., Sur P., Estep K., Lee A., Marczak L., Mokdad A.H., Moradi-Lakeh M., Naghavi M., Salama J.S., Vos T., Abate K.H., Abbafati C., Ahmed M.B., Al-Aly Z., Alkerwi A., Al-Raddadi R., Amare A.T., Amberbir A., Amegah A.K., Amini E., Amrock S.M., Anjana R.M., Ärnlöv J., Asayesh H., Banerjee A., Barac A., Baye E., Bennett D.A., Beyene A.S., Biadgilign S., Biryukov S., Bjertness E., Boneya D.J., Campos-Nonato I., Carrero J.J., Cecilio P., Cercy K., Ciobanu L.G., Cornaby L., Damtew S.A., Dandona L., Dandona R., Dharmaratne S.D., Duncan B.B., Eshrati B., Esteghamati A., Feigin V.L., Fernandes J.C., Fürst T., Gebrehiwot T.T., Gold A., Gona P.N., Goto A., Habtewold T.D., Hadush K.T., Hafezi-Nejad N., Hay S.I., Horino M., Islami F., Kamal R., Kasaeian A., V Katikireddi S., Kengne A.P., Kesavachandran C.N., Khader Y.S., Khang Y.-H., Khubchandani J., Kim D., Kim Y.J., Kinfu Y., Kosen S., Ku T., Defo B.K., Kumar G.A., Larson H.J., Leinsalu M., Liang X., Lim S.S., Liu P., Lopez A.D., Lozano R., Majeed A., Malekzadeh R., Malta D.C., Mazidi M., McAlinden C., McGarvey S.T., Mengistu D.T., Mensah G.A., Mensink G.B.M., Mezgebe H.B., Mirrakhimov E.M., Mueller U.O., Noubiap J.J., Obermeyer C.M., Ogbo F.A., Owolabi M.O., Patton G.C., Pourmalek F., Qorbani M., Rafay A., Rai R.K., Ranabhat C.L., Reinig N., Safiri S., Salomon J.A., Sanabria J.R., Santos I.S., Sartorius B., Sawhney M., Schmidhuber J., Schutte A.E., Schmidt M.I., Sepanlou S.G., Shamsizadeh M., Sheikhbahaei S., Shin M.-J., Shiri R., Shiue I., Roba H.S., Silva D.A.S., Silverberg J.I., Singh J.A., Stranges S., Swaminathan S., Tabarés-Seisdedos R., Tadese F., Tedla B.A., Tegegne B.S., Terkawi A.S., Thakur J.S., Tonelli M., Topor-Madry R., Tyrovolas S., Ukwaja K.N., Uthman O.A., Vaezghasemi M., Vasankari T., V Vlassov V., Vollset S.E., Weiderpass E., Werdecker A., Wesana J., Westerman R., Yano Y., Yonemoto N., Yonga G., Zaidi Z., Zenebe Z.M., Zipkin B., Murray C.J.L. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:13–27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1614362. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

