Proteomic profiling of Escherichia coli cytoplasmic proteins under sublethal boric acid stress
- PMID: 40678411
- PMCID: PMC12266352
- DOI: 10.55730/1300-0152.2745
Proteomic profiling of Escherichia coli cytoplasmic proteins under sublethal boric acid stress
Abstract
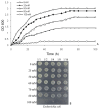
Background/aim: Boron is an essential micronutrient for plants and certain bacteria, where it plays critical roles in cellular processes at low concentrations. However, elevated levels of boron-containing compounds, such as boric acid, exhibit antimicrobial toxicity. Although the physiological effects of boric acid on bacteria have been partially characterized, its proteome-wide impacts remain poorly elucidated. This study employs a 2D-PAGE-based proteomic approach to investigate how sublethal boric acid stress alters the cytoplasmic proteome of Escherichia coli BW25113.
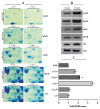
Materials and methods: E. coli BW25113 cultures were grown to mid-log phase in tryptic soy broth (TSB) and exposed to 70 mM boric acid (a sublethal concentration) or left untreated as a control. Cytoplasmic protein extracts were subjected to 2D-PAGE analysis to identify differentially expressed proteins. Selected protein spots were excised, identified via MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, and validated by RT-PCR to assess corresponding mRNA expression levels.
Results: Proteomic analysis revealed 12 differentially regulated cytoplasmic proteins under boric acid stress. Upregulated proteins included SodA, KduD, KduI, DeoB, Icd, AceE, RpsM, TdcE, Tuf1, LexA, and LamB, while GatY was downregulated. Functional annotation linked these proteins to oxidative stress defense (SodA), carbohydrate metabolism (KduD, KduI, DeoB), energy production (Icd, AceE), translation (RpsM, Tuf1), and membrane integrity (LamB). RT-PCR validation confirmed transcriptional upregulation of sodA, kduD, and kduI, corroborating proteomic findings. These results suggest that boric acid disrupts metabolic homeostasis, induces oxidative stress, and modulates structural and translational processes in E. coli.
Conclusion: This study provides the first proteomic evidence of E. coli's cytoplasmic response to boric acid stress, highlighting its multifaceted effects on metabolic, oxidative, and translational pathways. The upregulation of KduI and KduD, enzymes involved in carbohydrate utilization, points to potential adaptive mechanisms for boron detoxification. Further investigation into these targets could elucidate molecular strategies for bacterial boron tolerance and inform the development of boron-based antimicrobials.
Keywords: Boron stress; KduD; SodA; bacterial proteomics; metabolic adaptation.
© TÜBİTAK.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antibiotics versus topical antiseptics for chronic suppurative otitis media.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 9;6(6):CD013056. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013056.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40484400
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Citric acid impairs type B trichothecene biosynthesis of Fusarium graminearum but enhances its growth and pigment biosynthesis: transcriptomic and proteomic analyses.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Jun 18;91(6):e0153124. doi: 10.1128/aem.01531-24. Epub 2025 May 14. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40366181 Free PMC article.
-
Topical antiseptics for chronic suppurative otitis media.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 9;6(6):CD013055. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013055.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40484403
-
Single-cell proteomics analysis of human oocytes during GV-to-MI transition.Hum Reprod. 2025 Jul 1;40(7):1332-1343. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaf086. Hum Reprod. 2025. PMID: 40359387
References
-
- Avcı O, Sezer Kürkçü M, Çöl B, Sonay Elgin E, Anık Ü2023Development of a Highly Boron Tolerant Pseudomonas sp.–Fe-MOF Bioanode ChemistrySelect 845e202303350. 10.1002/SLCT.202303350 - DOI
-
- Babayeva A, Dibek E, Sünnetçi Akkoyunlu D, Çine N, Kasap M, et al. The effect of epetraborole on the transcriptome and proteome profiles of an Escherichia coli strain overexpressing leuS, Leucyl-tRNA Synthetase. Frontiers in Life Sciences and Related Technologies. 2024;5(1):48–58. doi: 10.51753/flsrt.1416938. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
