Deep learning enhanced deciphering of brain activity maps for discovery of therapeutics for brain disorders
- PMID: 40678509
- PMCID: PMC12268937
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112868
Deep learning enhanced deciphering of brain activity maps for discovery of therapeutics for brain disorders
Abstract
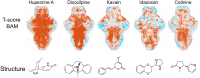
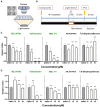
This study presents an artificial intelligence enhanced in vivo screening platform, DeepBAM, which enables deep learning of large-scale whole brain activity maps (BAMs) from living, drug-responsive larval zebrafish for neuropharmacological prediction. Automated microfluidics and high-speed microscopy are utilized to achieve high-throughput in vivo phenotypic screening for generating the BAM library. Deep learning is applied to deconvolve the pharmacological information from the BAM library and to predict the therapeutical potential of non-clinical compounds without any prior information about the chemicals. For a validation set composed of blinded clinical neuro-drugs, several potent anti-Parkinson's disease and anti-epileptic drugs are predicted with nearly 45% accuracy. The prediction capability of DeepBAM is further tested with a set of nonclinical compounds, revealing the pharmaceutical potential in 80% of the anti-epileptic and 36% of the anti-Parkinson predictions. These data support the notion of systems-level phenotyping in combination with machine learning to aid therapeutics discovery for brain disorders.
Keywords: Biomedical Engineering; Pharmacology.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
P.S. is listed as an inventor on a patent (US 9,897,593) filed by the City University of Hong Kong describing the system for automated handling of larval zebrafish. S.J.H. has served or serves on the advisory board of Proximity Therapeutics, Psy Therapeutics, Frequency Therapeutics, Souvien Therapeutics, Sensorium Therapeutics, 4M Therapeutics, Ilios Therapeutics, Entheos Labs, the Alzheimer’s Disease Drug Discovery Foundation, and the Kissick Family Foundation FTD grant program, none of whom were involved in the present study. S.J.H. has also received speaking or consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Merck, Regenacy Pharmaceuticals, Syros Pharmaceuticals, and Juvenescence Life, as well as sponsored research or gift funding from AstraZeneca, JW Pharmaceuticals, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Vesigen Therapeutics, Compass Pathways, Atai Life Sciences, and Stealth Biotherapeutics. The funders had no role in the design or content of this article or the decision to submit this review for publication.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Development and Validation of a Convolutional Neural Network Model to Predict a Pathologic Fracture in the Proximal Femur Using Abdomen and Pelvis CT Images of Patients With Advanced Cancer.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023 Nov 1;481(11):2247-2256. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002771. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023. PMID: 37615504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Danon J.J., Reekie T.A., Kassiou M. Challenges and Opportunities in Central Nervous System Drug Discovery. Trends Chem. 2019;1:612–624. doi: 10.1016/j.trechm.2019.04.009. - DOI
-
- de Lange E.C.M., van den Brink W., Yamamoto Y., de Witte W.E.A., Wong Y.C. Novel CNS drug discovery and development approach: model-based integration to predict neuro-pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017;12:1207–1218. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2017.1380623. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

