A systematic review via text mining approaches of human and veterinary applications of photobiomodulation: focus on multiwave locked system laser therapy
- PMID: 40679542
- PMCID: PMC12274228
- DOI: 10.1007/s10103-025-04572-y
A systematic review via text mining approaches of human and veterinary applications of photobiomodulation: focus on multiwave locked system laser therapy
Abstract
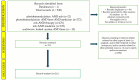
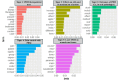
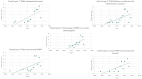
To evaluate scientific literature regarding the application of Photobiomodulation (PBM), with a special focus on Multiwave Locked System (MLS®) laser therapy, an innovative machine learning method was used. PBM therapy has occurred as a non-invasive therapeutic approach in human and veterinary medicine. It is widely used to treat various musculoskeletal conditions, promote wound healing, and alleviate inflammation and pain through cellular modulation mechanisms.The methods used were text mining (TM) and topic analysis (TA) to store and process large datasets in digital formats. The investigation followed a systematic approach based on the PRISMA guidelines. Our analysis of 211 selected studies, conducted from 1990 to 2024, identified five key topics in PBM research: therapeutic uses, cellular effects and mechanisms of action, pain control, outcomes in oral pathologies, and laser biostimulation of wounds and bones. Notably, research highlights the effectiveness of MLS® in musculoskeletal pain management, neuropathic conditions, and complex wound care, both in human and veterinary medicine. Despite increasing evidence supporting its clinical applications, significant gaps remain regarding standardized treatment protocols and a deeper understanding of molecular mechanisms.Further research is necessary to elucidate optimal parameters for different clinical applications, with particular emphasis on individualized dosing, frequency, and treatment duration, to maximize therapeutic outcomes.
Keywords: Laser therapy; Multiwave-locked system; Photobiomodulation; Text mining; Topic analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Figures

References
-
- Dompe C, Moncrieff L, Matys J, Grzech-Leśniak K, Kocherova I, Bryja A, Bruska M, Dominiak M, Mozdziak P, Skiba THI, Shibli JA, Angelova Volponi A, Kempisty B, Dyszkiewicz-Konwińska M (2020) Photobiomodulation-Underlying mechanism and clinical applications. J Clin Med 9(6):1724. 10.3390/jcm9061724 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pryor B, Millis DL (2015) Therapeutic laser in veterinary medicine. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract 45(1):45–56. 10.1016/j.cvsm.2014.09.003 - PubMed
-
- Young NC, Maximiano V, Arany PR (2022) Thermodynamic basis for comparative photobiomodulation dosing with multiple wavelengths to direct odontoblast differentiation. J Biophotonics 15(6):e202100398. 10.1002/jbio.202100398 - PubMed
-
- Parker S, Anagnostaki E, Mylona V, Cronshaw M, Lynch E, Grootveld M (2020) Systematic review of post-surgical laser-assisted oral soft tissue outcomes using surgical wavelengths outside the 650–1350 Nm optical window. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg 38(10):591–606 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

