Dynamic rewiring of microRNA networks in the brainstem autonomic control circuits during hypertension development in the female spontaneously hypertensive rat
- PMID: 40679600
- PMCID: PMC12341004
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00136.2024
Dynamic rewiring of microRNA networks in the brainstem autonomic control circuits during hypertension development in the female spontaneously hypertensive rat
Abstract
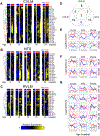
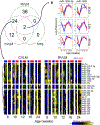
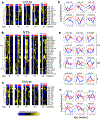
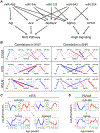
We describe global miRNA changes in the central autonomic control circuits during the development of neurogenic hypertension. Using the female spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR) and the normotensive Wistar Kyoto (WKY), we analyzed the dynamic miRNA expression changes in three brainstem regions, the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS), caudal ventrolateral medulla (CVLM), and rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) as a time series beginning at 8 weeks of age prior to hypertension onset through to extended chronic hypertension. Our analysis yielded nine miRNAs that were significantly differentially regulated in all three regions between SHR and WKY over time. We collated computationally predicted gene targets of these nine miRNAs in pathways related to neuronal plasticity and autonomic regulation to construct a putative miRNA target gene network involved in the development of neurogenic hypertension. We analyzed the dynamic correlations between the miRNAs and their putative targets to identify the regulatory interactions shifting between WKY and SHR. Comparing the results with previously published data in male SHR and WKY identified miRNA network dynamics specific to female SHR during hypertension development. Collectively, our results point to distinct rewiring of the miRNA regulatory networks governing angiotensin signaling and homeostasis, neuronal plasticity, and inflammatory processes contributing to the development of hypertension in female SHR.
Keywords: Autonomic Control Circuits; Neurogenic hypertension; Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat; microRNA networks; microRNA profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
RCAN1-Mediated Calcineurin Impairment Drives Sympathetic Outflow in Hypertension.Circ Res. 2025 Jul 18;137(3):417-434. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.325975. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Circ Res. 2025. PMID: 40510021
-
Dynamic dysregulation of transcriptomic networks in brainstem autonomic nuclei during hypertension development in the female spontaneously hypertensive rat.Physiol Genomics. 2024 Mar 1;56(3):283-300. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00073.2023. Epub 2023 Dec 25. Physiol Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38145287 Free PMC article.
-
A MicroRNA Screen Identifies the Wnt Signaling Pathway as a Regulator of the Interferon Response during Flavivirus Infection.J Virol. 2017 Mar 29;91(8):e02388-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02388-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28148804 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical interventions for treating extracapsular hip fractures in older adults: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 10;2(2):CD013405. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013405.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35142366 Free PMC article.
-
Convergent and divergent evolution of microRNA-mediated regulation in metazoans.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2024 Apr;99(2):525-545. doi: 10.1111/brv.13033. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2024. PMID: 37987240 Review.
References
-
- Badawy H, Mesbah N, Abo-El-Matty D. A Brief review of Circulating MicroRNAs and Essential Hypertension. Records of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences 2: 32–45, 2018. 10.21608/rpbs.2018.5986.1016. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

